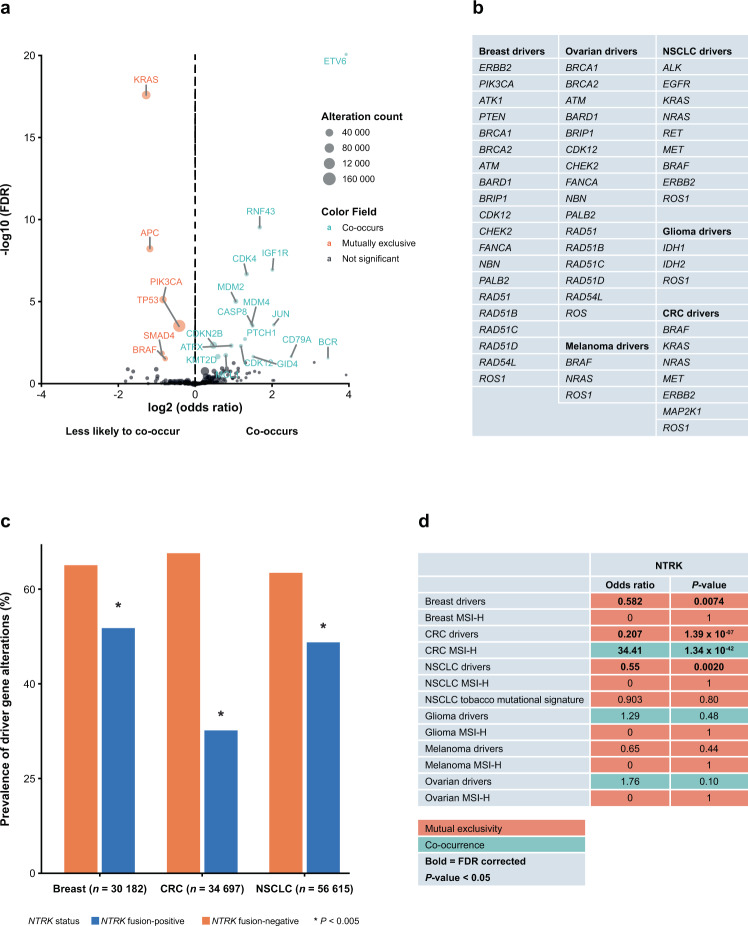
Fig. 3. Co-occurrence of genes among NTRK fusion-positive cancers.
Co-occurrence of genes in all NTRK fusion-positive cancers (a). The prevalence of gene mutations was compared for NTRK fusion-positive and fusion-negative disease. Co-occurrence refers to genes that occurred in NTRK fusion-positive disease with an odds ratio greater than 1 compared with NTRK fusion-negative disease and the false discovery rate (FDR)-adjusted P-value was <0.05. Lack of co-occurrence refers to genes that did not occur in NTRK fusion-positive disease with an odds ratio less than 1 compared with NTRK fusion-negative disease and the FDR-adjusted P-value was <0.05. List of known disease-specific driver genes for different tumour types (b). The frequency of mutations found within driver genes listed in b in NTRK fusion-positive and NTRK fusion-negative colorectal cancer (CRC), breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC; c). Summary of co-occurrence and mutual exclusivity of driver gene mutations and microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) status with specific NTRK fusion-positive cancers (d). NTRK neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase.