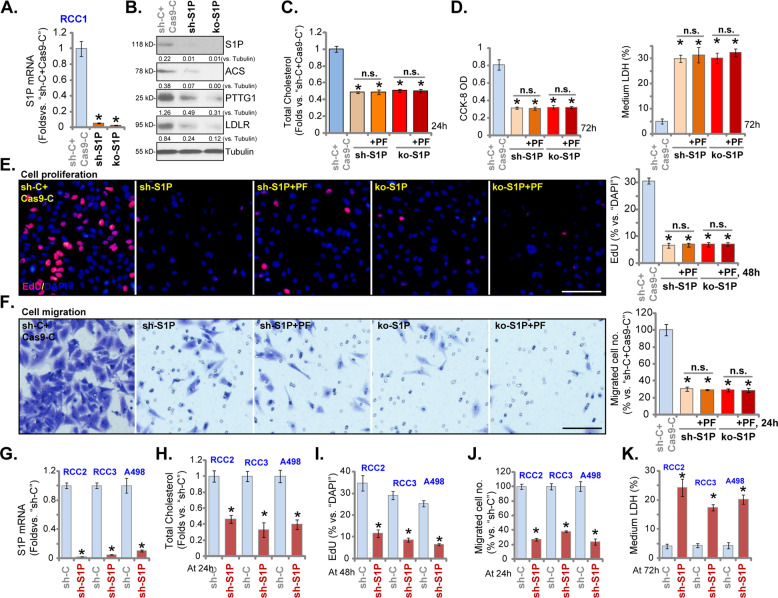
Fig. 3. S1P silencing or knockout inhibits RCC cell growth.
Stable RCC1 cells expressing S1P lentiviral shRNA (“sh-S1P” cells) or the CRSPR/Cas9-S1P-KO-GFP construct (“ko-S1P” cells) were established, control cells were transduced with scrambled control shRNA plus CRSPR/Cas9 empty vector (“sh-C + Cas9-C”); Expression of listed genes was shown (A and B); Cells were then treated with or without PF-429242 (10 μM), and cultured for applied time periods, total cholesterol levels were tested (C); Viable cell number, cell death, proliferation, and migration were tested by CCK-8 (D), LDH release (D), nuclear EdU staining (E) and “Transwell” (F) assays, respectively, and results were quantified.RCC2, RCC3, and A498 cells, expressing S1P lentiviral shRNA (“sh-S1P” cells) or scramble control shRNA (“sh-C”), were established and S1P mRNA expression was shown (G); Cells were further cultured for applied time periods, total cholesterol levels were tested (H); Cell proliferation, migration, and cell death were tested by nuclear EdU staining (I), “Transwell” (J) and medium LDH release (K) assays, respectively. For each assay, n = 5. Data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD).* P < 0.05 vs. “sh-C + Cas9-C”/“sh-C” group. “n.s.” stands for no statistical difference (C–F). In this figure, experiments were repeated three times, and similar results were obtained each time. Scale bar = 100 μm (E and F).