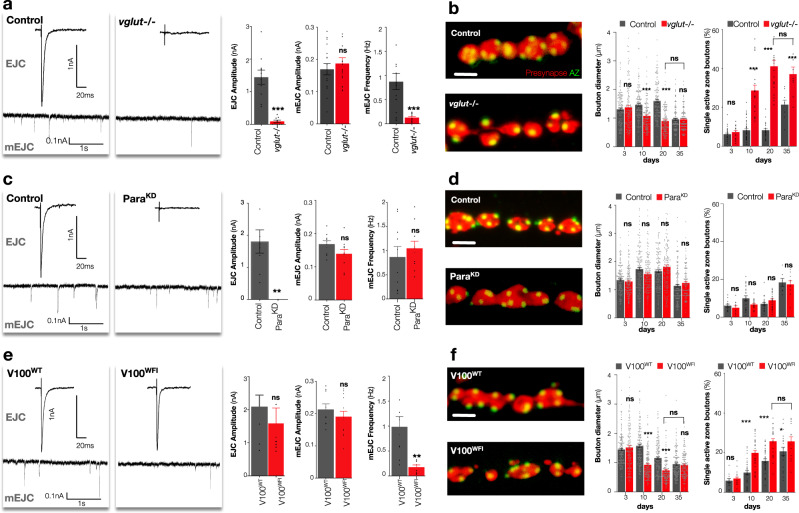
Fig. 3. Miniature but not evoked neurotransmission is required for adult synapse maintenance.
a Representative EJC (above) and mEJC (below) traces, quantification of EJC amplitude, mEJC amplitude and frequency of control [UAS > GFP/+; HB9 > Gal4, Tub > Gal80ts] and HB9 neuron selective adult conditional vglut−/− mutants [Df(2R)371/B3RT_vglut_B3RT; HB9 > Gal4, UAS > GFP, Tub > Gal80ts/UAS > B3] at 20 days after eclosion. b Representative images of presynaptic HB9 neuron boutons (red, GFP) and active zones (Brp, green), quantification of bouton diameters and percentage of boutons with only a single active zone (bouton fragmentation) of control and vglut mutants until 35 days after eclosion. c Representative EJC and mEJC traces, quantification of EJC amplitude, mEJC amplitude and frequency of control [UAS > luciferaseRNAi/HB9 > Gal4, UAS > GFP, Tub > Gal80ts] and HB9 neuron selective adult conditional Para knockdown mutants (ParaKD) [UAS > GFP/+; HB9 > Gal4, Tub > Gal80ts/UAS > ParaRNAi] at 20 days after eclosion. d Representative images of presynaptic HB9 neuron boutons and active zones, quantification of bouton diameters and bouton fragmentation as measured by the percentage of boutons with only a single active zone of control and ParaKD mutants until 35 days after eclosion. e Representative EJC and mEJC traces, quantification of EJC amplitude, mEJC amplitude and frequency of HB9 neuron selective adult conditional V100WT [UAS > V1003′UTR_RNAi/UAS > V100WT; HB9 > Gal4, UAS > GFP, TubGal80ts] and V100WFI mutants [UAS > V1003′UTR_RNAi/UAS > V100WFI; HB9 > Gal4, UAS > GFP, TubGal80ts] at 20 days after eclosion. f Representative images of presynaptic HB9 neuron boutons and active zones, quantification of bouton diameters and percentage of boutons with only a single active zone of V100WT and V100WFI mutants until 35 days after eclosion. Unpaired two-tailed t-test, ***p < 0.001, n ≥ 9 presynaptic terminals per timepoint (a, EJC amplitude), p = 0.249, n ≥ 17 presynaptic terminals per timepoint (a, mEJC amplitude), ***p < 0.001, n ≥ 17 presynaptic terminals per timepoint (a, mEJC frequency), ***p < 0.001, n ≥ 6 presynaptic terminals per timepoint (c, EJC amplitude), p = 0.09, n ≥ 10 presynaptic terminals per timepoint (c, mEJC amplitude), p = 0.5, n ≥ 10 presynaptic terminals per timepoint (c, mEJC frequency), p = 0.4, n ≥ 8 presynaptic terminals per timepoint (e, EJC amplitude), p = 0.06, n ≥ 8 presynaptic terminals per timepoint (e, mEJC amplitude), **p = 0.004, n ≥ 8 presynaptic terminals per timepoint (e, mEJC frequency). Two-way ANOVA, followed by Sidak’s multiple comparison tests were used to compare the mean of control and experimental genotypes in that timepoint, ns = not significant, ***p ≤ 0.001, n = 150 boutons per timepoint (b, bouton diameters), ns not significant, ***p < 0.001, n ≥ 9 presynaptic terminals per timepoint (b, single active zone boutons), ns not significant, n = 150 boutons per timepoint (d, bouton diameters), ns not significant, n ≥ 9 presynaptic terminals per timepoint (d, single active zone boutons), ns = not significant, ***p ≤ 0.001, n = 150 boutons per timepoint (f, bouton diameters), ns not significant, ***p < 0.001, n ≥ 14 presynaptic terminals per timepoint (f, single active zone boutons). All statistical analysis details with a precise value of ‘n’ are reported in Supplementary Tables 4 and 5 and in Source Data file. Scale bar = 2 μm (b, d, f). Experiments were carried out at 29 °C. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. n = biologically independent samples.