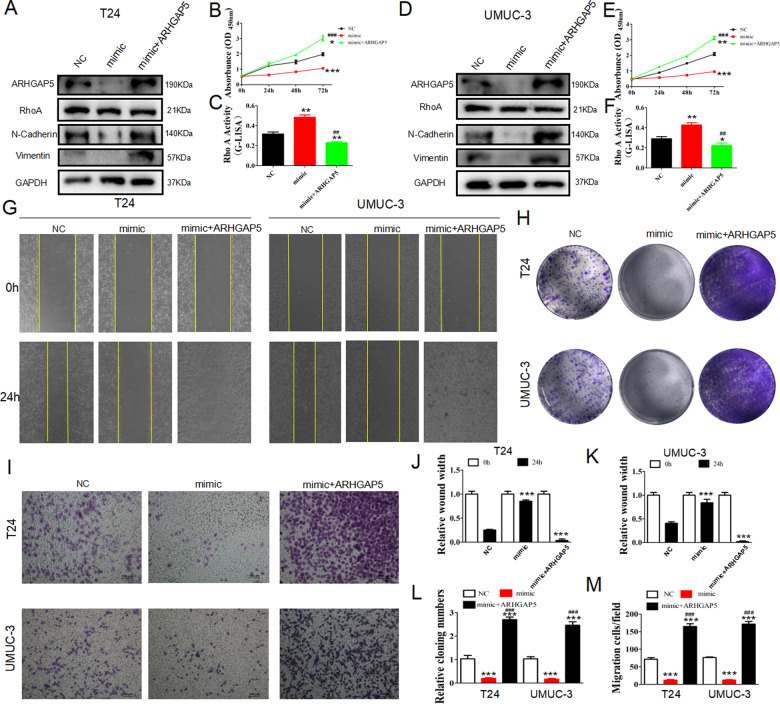
Fig. 6. Upregulation of ARHGAP5 rescued the ability of proliferation and invasiveness of BC cells after miR-516b-5p overexpression.
T24 and UM-UC-3 cells were transfected with empty vector (NC), hsa-miR-516b-5p mimics (mimic), hsa-miR-516b-5p mimics together with ARHGAP5 overexpression vector (mimic+ARHGAP5). (A, D) Cells were then subjected to western blot analysis with anti-ARHGAP5, anti-N-Cadherin, anti-Vimentin and anti-GAPDH. GAPDH was used as loading control. (B, E) CCK-8 assays of transfected T24 and UM-UC-3 cells at 0 h, 24 h, 48 h and 72 h after transfection were performed (***P < 0.001,**P < 0.01,*P < 0.05 versus NC, ###P < 0.001 versus si-circUBE2K) (C and F) RhoA G-LISA activation assays were used to evaluate RhoA activity in transfected T24 and UM-UC-3 (**P < 0.01,*P < 0.05 versus NC, ##P < 0.01 versus si-circUBE2K). (G, J, K) Wound healing assays at 0 h and 24 h were done to assess cell migration ability (Left panel: T24-NC, T24-mimic, T24-mimic+ARHGAP5; Right panel: UM-UC-3-NC, UM-UC-3-mimic, UM-UC-3-mimic+ARHGAP5) (***P < 0.001 versus NC). (H, L) Colony formation assays of transfected T24 and UM-UC-3 were carried out to test cell proliferation potential.(***P < 0.001 versus NC, ###P < 0.001 versus si-circUBE2K) (I, M) Transwell cell migration assays of transfected T24 and UM-UC-3 were carried out to evaluate cell invasion ability(***P < 0.001 versus NC, ###P < 0.001 versus si-circUBE2K).