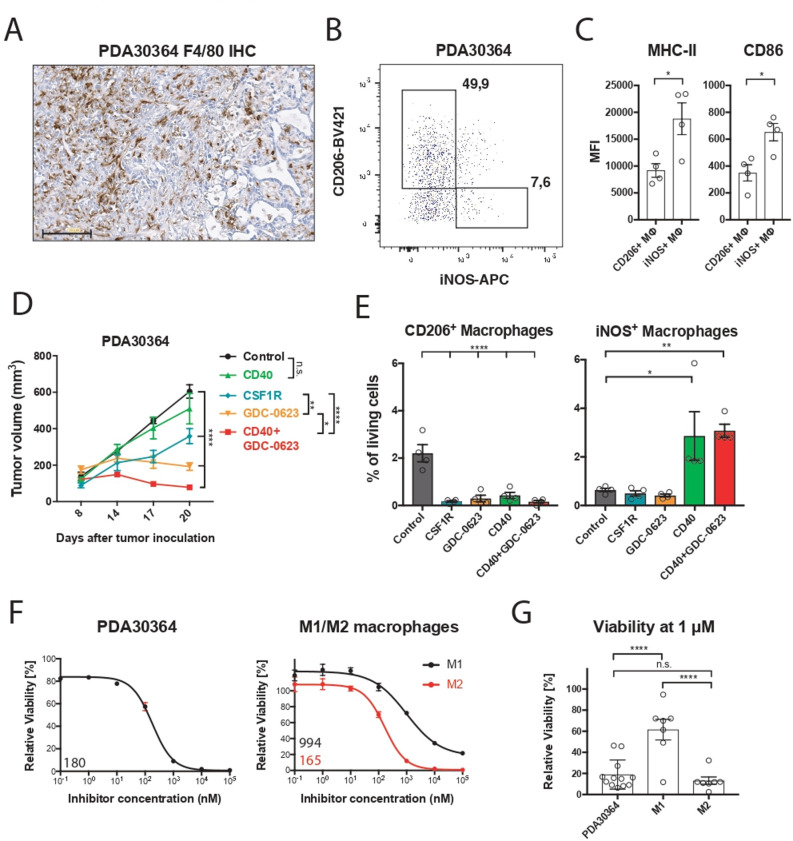
Figure 1.
M2 macrophages are highly sensitive to MEK inhibition in vivo and ex vivo. (A) Immunohistochemistry of a PDA30364 tumor using an F4/80-specific antibody. Scale bar: 100 µm. (B) Flow cytometric identification of iNOS+ M1 and CD206+ M2 macrophages in a freshly dissociated tumor sample upon gating on the live CD45+, CD11b+, F4/80+ cell subset. (C) MHC-II (IA/IE) and CD86 surface levels of macrophages gated in (B). Mean±SEM, n=4. (D) Mice bearing PDA30364 tumors were treated with MEKi 30 mg kg−1 GDC-0623 (daily), anti-CSF1R antibody (1 mg once, followed by 0.5 mg every other day), or anti-CD40 antibody (200 µg on days 10, 12, 14, and 17 after tumor inoculation). Mean±SEM, n=5. Two-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test. (E) Flow cytometry-based quantification of M2 (CD206+) and M1 (iNOS+) macrophages in PDA30364 tumors from mice treated as described in (C). Mean±SEM, n=4. One-way ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett test. (F) Dose–response curves of PDA30364 and M1 (20 ng mL−1 M-CSF+1 ng mL−1 IFNγ/LPS) and M2 (20 ng mL−1 M-CSF+2.5 ng mL−1 IL-4) polarized murine macrophages treated with GDC-0623. Mean±SEM, n=3. Numbers indicate best-fit inhibitory concentration (IC)50 values. (G) Viability of PDA30364 and murine M1 and M2 macrophages treated with GDC-0623 at 1 µM. Mean±SEM, n>4. One-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test. Significance levels are indicated by asterisks (*p≤0.05; **p≤0.01; ***p≤0.001: ****p≤0.0001). ANOVA, analysis of variance; IFNγ, interferon-γ; IL, interleukin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; M-CSF, macrophage-colony stimulating factor; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase.