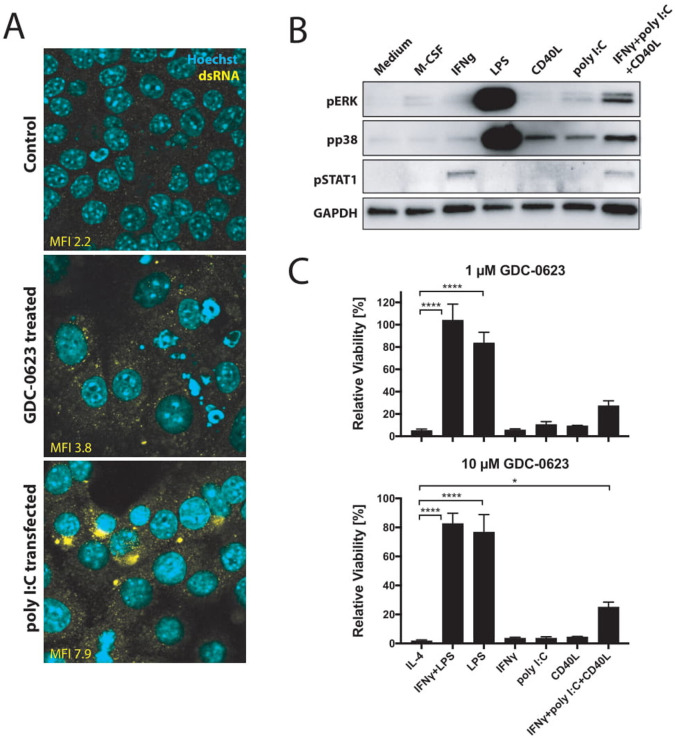
Figure 4.
CD40 ligation and dsRNA treatment stimulate p38 signaling in macrophages. (A) Immunofluorescence analysis of dsRNA untreated or treated with 1 µM GDC-0623 for 48 hours. Poly I:C transfection served as a positive straining control. (B) Western blot of mouse BMDM stimulated with culture medium containing 20 ng mL−1 M-CSF, 10 ng mL−1 IFNγ, 1 ng mL−1 LPS, 1 µg mL−1 CD40L, 100 ng mL−1 poly I:C, or the combination of 10 ng mL−1 IFNγ+100 ng mL−1 poly I:C+1 µg mL−1 CD40L. (C) Viability of differently stimulated macrophages (20 ng mL−1 M-CSF+2.5 ng mL−1 IL-4, 10 ng mL−1 IFNγ+1 ng mL−1 LPS, 1 ng mL−1 LPS, 10 ng mL−1 IFNγ, 100 ng mL−1 poly I:C, 1 µg mL−1 CD40L, or the combination of 10 ng mL−1 IFNγ+100 ng mL−1 poly I:C+1 µg mL−1 CD40L) treated with GDC-0623 for 3 days. Mean±SEM, n=3. One-way ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett test. Significance levels are indicated by asterisks (*p≤0.05; ****p≤0.0001). ANOVA, analysis of variance; BMDM, bone marrow-derived macrophages; dsRNA, double-stranded RNA; IFNγ, interferon-γ; IL, interleukin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; M-CSF, macrophage-colony stimulating factor; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase.