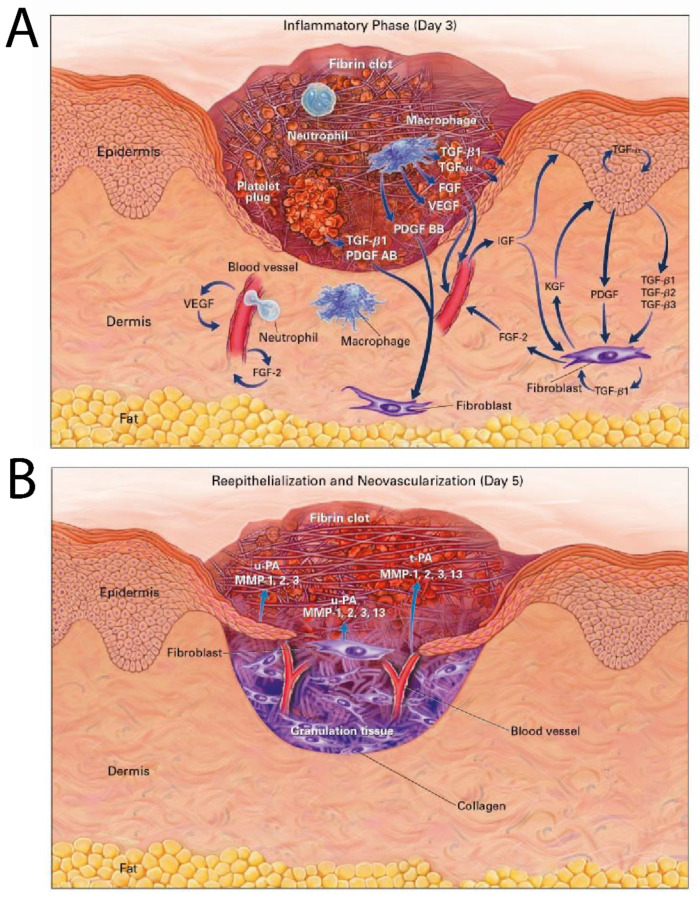
Figure 1.
(A) A cutaneous wound 3 days after injury. Growth factors thought to be necessary for cell movement into the wound are shown. TGF-β1, TGF-β2, and TGF-β3 denote transforming growth factor β1, β2, and β3, respectively; TGF-α transforming growth factor α; FGF fibroblast growth factor; VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor; PDGF, PDGF AB, and PDGF BB platelet-derived growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor AB, and platelet-derived growth factor BB, respectively; IGF insulin-like growth factor; and KGF keratinocyte growth factor. (B) A cutaneous wound 5 days after injury. Blood vessels are seen sprouting into the fibrin clot as epidermal cells resurface the wound. Proteinases thought to be necessary for cell movement are shown. The abbreviation u-PA denotes urokinase-type plasminogen activator; MMP-1, 2, 3, and 13 matrix metalloproteinases 1, 2, 3, and 13 (collagenase 1, gelatinase A, stromelysin 1, and collagenase 3, respectively); and t-PA tissue plasminogen activator. Images reproduced with permission from [4].