Table 2.
Genetic variability and importance of the main CYP isoenzymes involved the metabolism of xenobiotics.
| CYCYP Isoenzyme | Polymorphism Frequency | Functional Effects | Allelic Variants | Participation in the Metabolism of Xenobiotics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A1 | Relatively high | Rare | 13 |
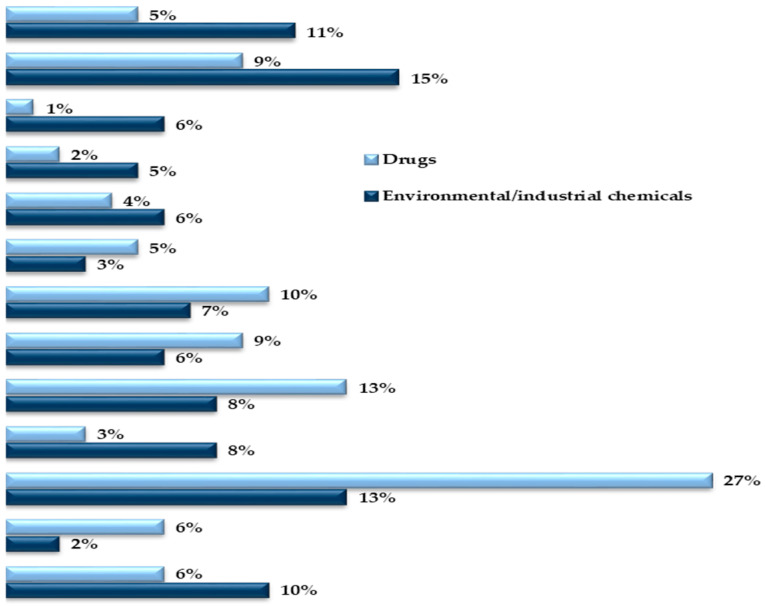
|
| 1A2 | High | Rare | 21 | |
| 1B1 | Frequent missense mutations | Rare | 26 | |
| 2A6 | Higher in Orientals than in Caucasians | Significant | 45 | |
| 2B6 | High | Significant | 38 | |
| 2C8 | High | Significant | 14 | |
| 2C9 | Relatively rare in Caucasians | Very significant | 70 | |
| 2C19 | High | Very significant | 38 | |
| 2D6 | Very High | Highly significant | 145 | |
| 2E1 | Low | No significance | 7 | |
| 3A4 | Low | Low significance | 32 | |
| 3A5 | High | Significant | 9 | |
| Other (a) | - | - | - |
(a) Other CYP isoenzymes involved in smaller fraction of xenobiotic metabolism (2A13, 2C18, 2F1, 2J2, 3A7 and some members of the CYP4 family). Due to substrate overlapping specificity, CYP1B1 (typical sterols metabolizer) and 2J2 (typical fatty acids metabolizer) were also included in the CYP xenobiotic metabolizer analysis.
