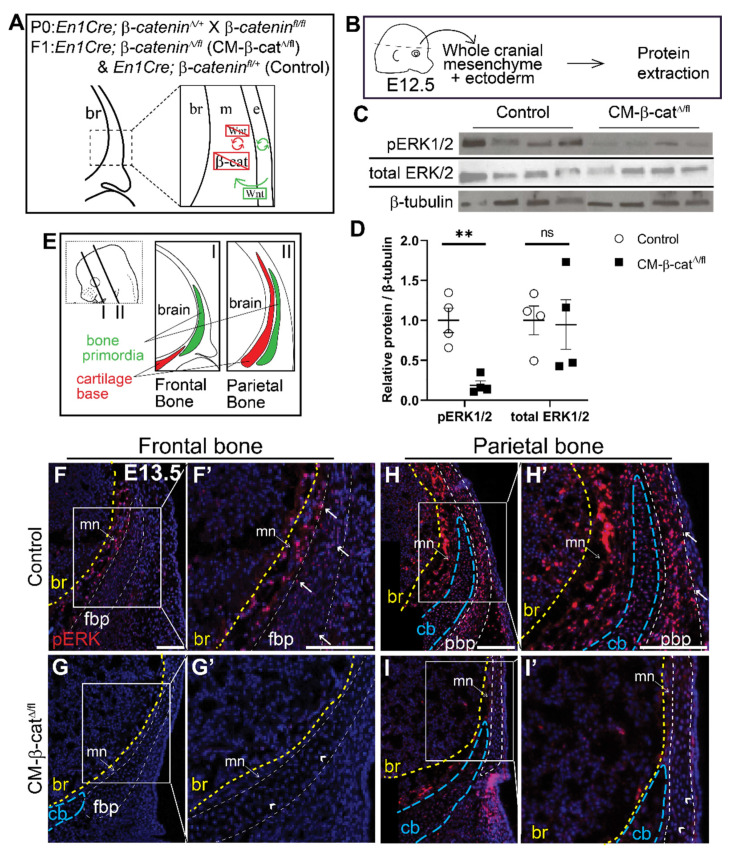
Figure 3.
ERK signaling is diminished in CM-β-catΔ/flmutants. (A) Schematic depicting the status of Wnt signaling in the cranial mesenchyme and overlying ectoderm in this mouse model of Wnt signaling deletion. br, brain; m, mesenchyme; e, ectoderm. β-catenin is deleted in the cranial mesenchyme preventing mesenchyme Wnt signaling. The ectoderm is able to secrete Wnt ligands and undergo Wnt signaling. (B) Schematic depicting the work flow and tissue source for the protein analysis in panels C and D. (C,D) Expression of activated ERK1/2 (pERK1/2) and total ERK1/2 relative to β-tubulin expression in En1Cre;β-cateninfl/+ (control) and En1Cre;β-cateninΔ/fl (CM-β-catΔ/fl) normalized to control. p(**) = 0.0026 (E) Schematic indicating the plane and orientation of specimens. (F–I’) Immunofluorescence staining of pERK1/2 in control and CM-β-catΔ/fl coronal sections at E13.5 in the frontal (F–G’) and parietal bone regions (H–I’). Yellow lines demarcate the br, brain; blue lines demarcate the cb, cartilage base; mn, meninges. Arrows denote pERK1/2 signal in the bone primordia of the controls and arrowheads denote lack of signal in the CM-β-catΔ/fl. fpb, frontal bone primordia; pbp, parietal bone primordia; n = 4.