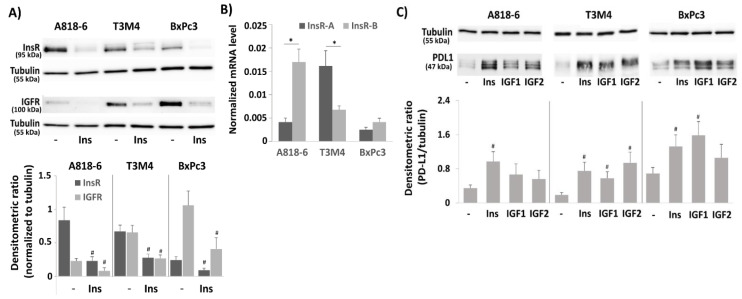
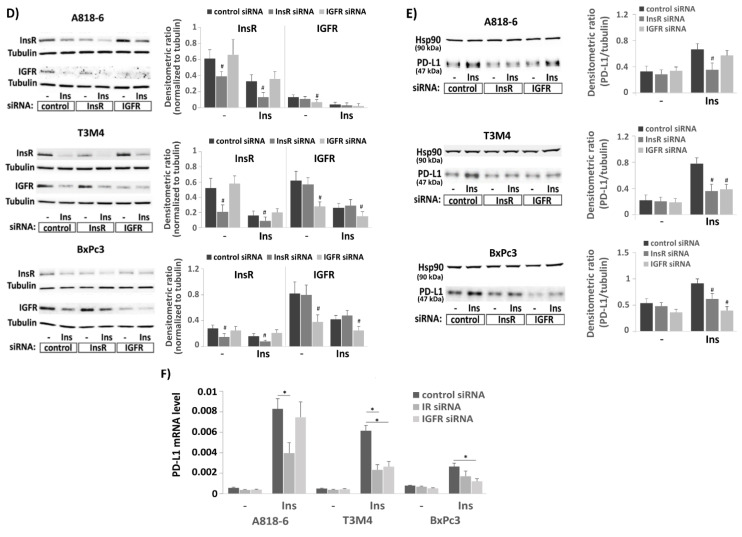
Figure 2.
Involvement of insulin receptors (InsR) and IGF receptors (IGFR) in the insulin-induced PD-L1 expression in PDAC cell lines. (A–C) Serum-starved A818-6, T3M4, and BxPc3 cells were either left untreated (B) or were treated (A) with 0.1 IU/mL insulin for 24 h and (C), with 0.1 IU/mL insulin, 0.1 µg/mL IFG1, or 0.1 µg/mL IGF2 for 24 h. (A,C) Western blot analysis using (A) InsR and tubulin or (C) PD-L1 and tubulin antibodies. Representative blots from four independent experiments and band densitometry analyses (lower panels, # p < 0.05 compared to untreated, n = 4) are shown. (B) qPCR analysis using InsR-A, InsR-B, and RPL13 primers. InsR-A and InsR-B expression was normalized to the expression level of RPL13, and data represent the mean ± SD from five independent experiments (* p < 0.03 compared to untreated). (D–F) A818-6, T3M4, and BxPc3 cells were pretreated with control, InsR, or IGFR siRNA for 48 h, followed by treatment with 0.1 IU/mL insulin or without for 24 h. (D,E) Western blot analysis using (D) InsR, IGFR, and tubulin or (E) PD-L1 and Hsp90 antibodies. Representative blots from four independent experiments and band densitometry analyses (right panels, # p < 0.05 compared to control siRNA, n = 4) are shown. (F) qPCR analysis using PD-L1 and RPL13 primers. PD-L1 expression was normalized to the expression level of RPL13, and data represent the mean ± SD from five independent experiments (* p < 0.03 compared to control siRNA).