Figure 4:
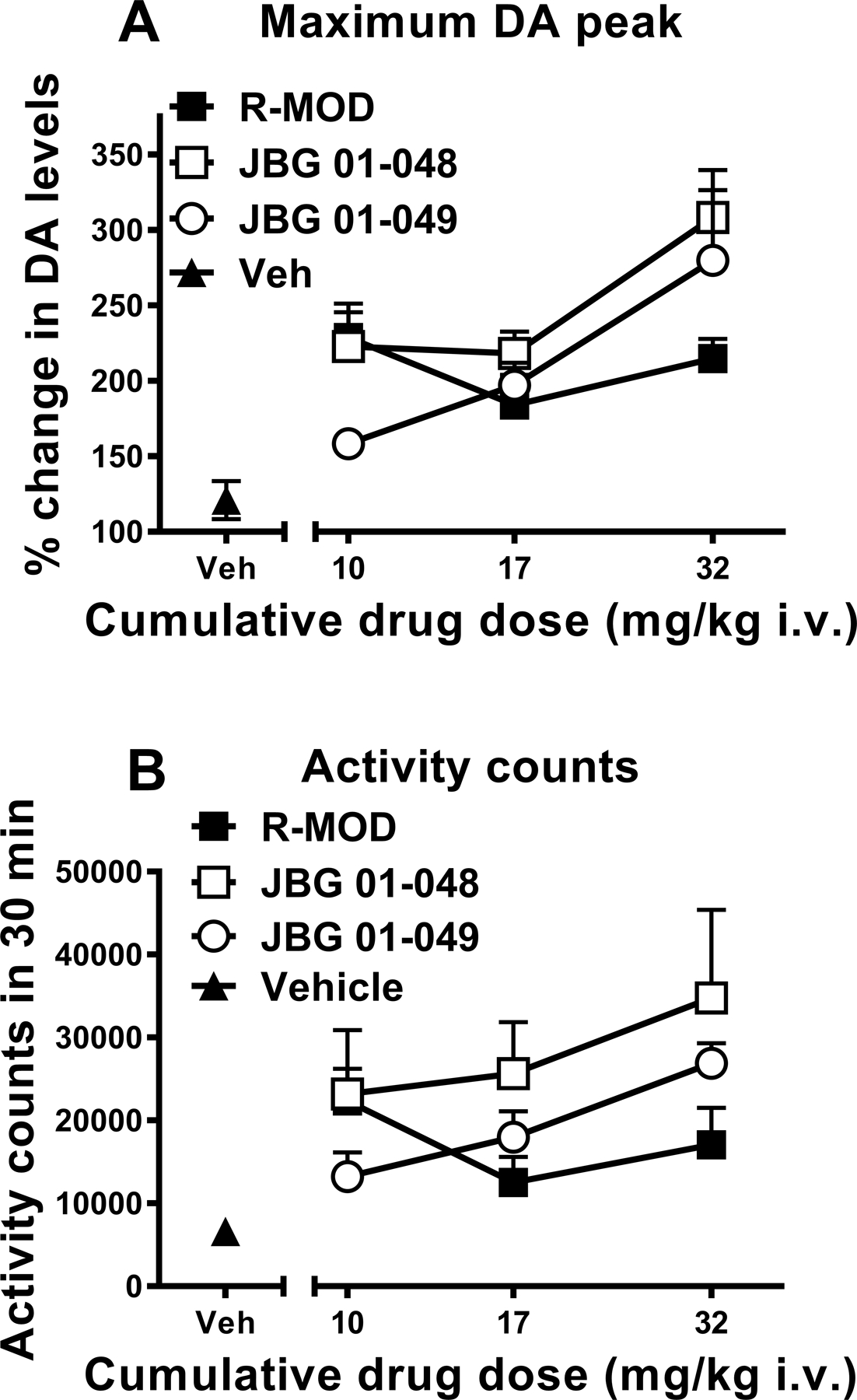
Panel (A): Maximum increase in DA levels in dialysates from the NAS in rats obtained following intravenous administration of cumulative doses (10–32 mg/kg) of R-MOD, JBG1–048 and JBG1–049, or their vehicle (2ml/kg). The effects of R-MOD resemble those already reported for MOD and its enantiomers in mice (Loland et al., 2012), where the slope of the dose-response curve was shallow as compared to that for a widely abused psychostimulant like cocaine. Results are means, with vertical bars representing SEM, of the amount of DA in 10-min dialysate samples, expressed as percentage of basal values, uncorrected for probe recovery.
Panel (B): Behavioral activity counts obtained during the first 30 minutes after each intravenous administration of cumulative doses (10–32 mg/kg) of R-MOD, JBG1–048 and JBG1–049, or their vehicle (2ml/kg). Our results show that the pattern of changes in behavioral effects related to these drugs appears similar to the pattern of changes in maximum increase in DA levels obtained with the same cumulative drug doses shown on panel A.
