Figure 1:
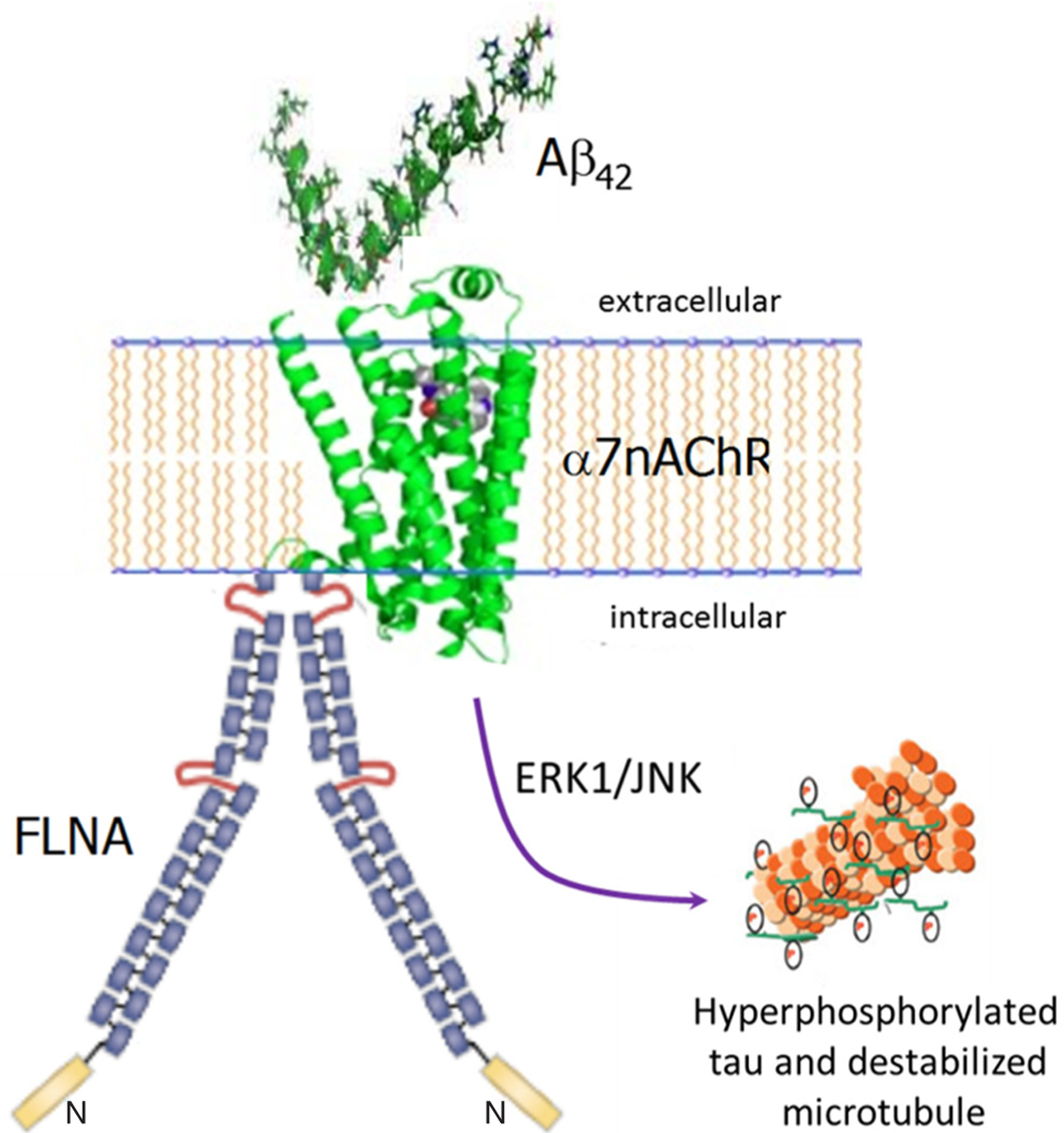
Altered FLNA linkage to α7nAChR enables Aβ42’s toxic signaling via α7nAChR to hyperphosphorylate tau. Monomers or small oligomers of Aβ42 bind α7nAChR, which recruits FLNA to link to α7nAChR. This recruitment likely alters FLNA’s conformation, which in turn increases the affinity of the Aβ42-α7nAChR interaction to a femtomolar affinity and enables the signaling. ERK1 and JNK kinases are activated to hyperphosphorylate tau. Hyperphosphorylated tau loses its function of stabilizing microtubules and dissociates from them, eventually creating PHFs and neurofibrillary tangles. FLNA: filamin A; Aβ: amyloid beta; α7nAChR: α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; PHF: paired helical filament
