Figure 2:
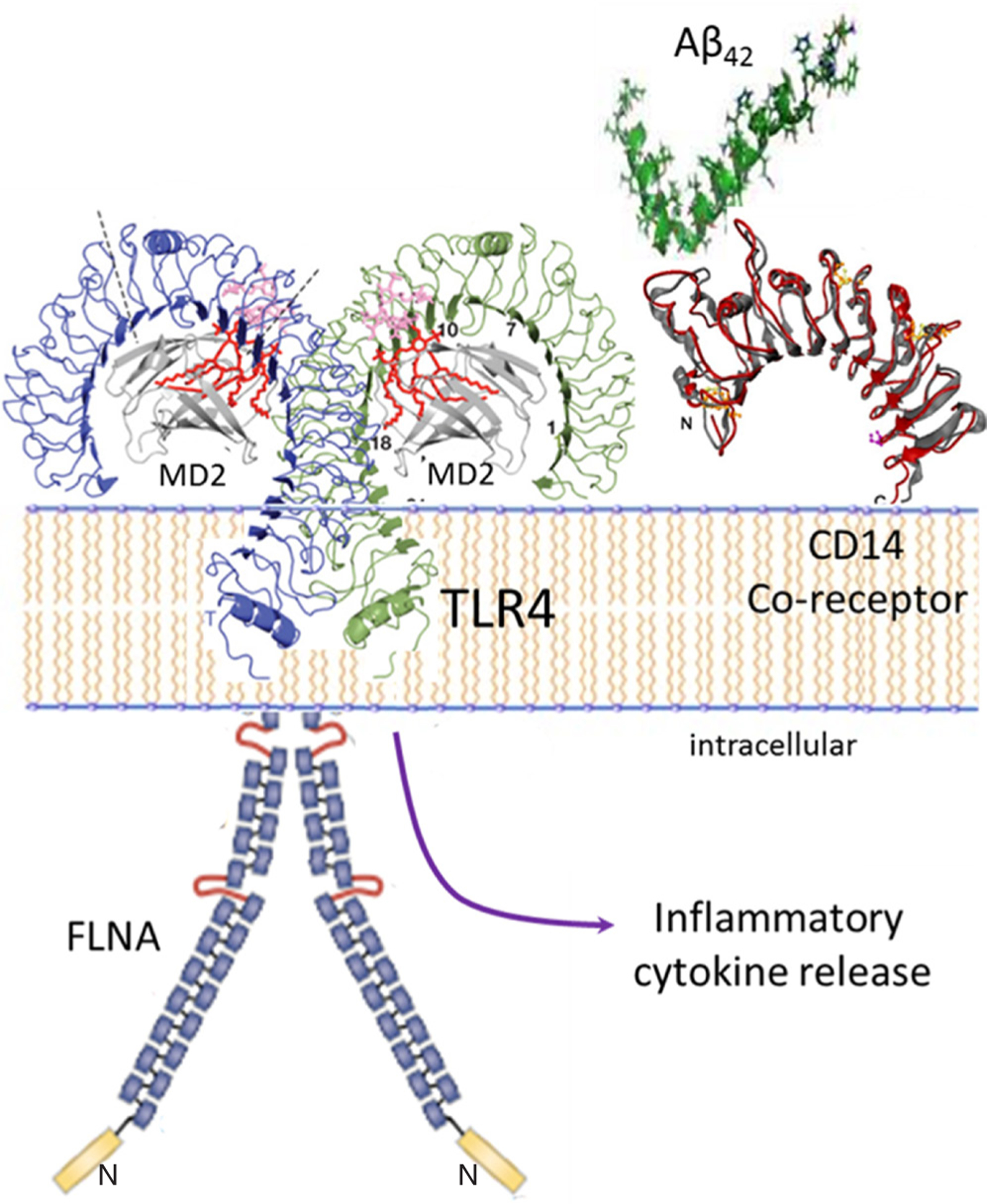
Altered FLNA linkage to TLR4 enables persistent Aβ42-induced TLR4 activation and neuroinflammation. Aβ42 binds the CD14 co-receptor to induce FLNA recruitment to TLR4. As with α7nAChR, the FLNA linkage likely alters the FLNA conformation. With Aβ42 binding CD14, altered FLNA linkage to TLR4 enables a sustained TLR4 activation, leading to substantial inflammatory cytokine release and the neuroinflammation characteristic of AD. FLNA: filamin A; Aβ: amyloid beta; α7nAChR: α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; TLR4: toll-like-receptor 4
