Figure 4.
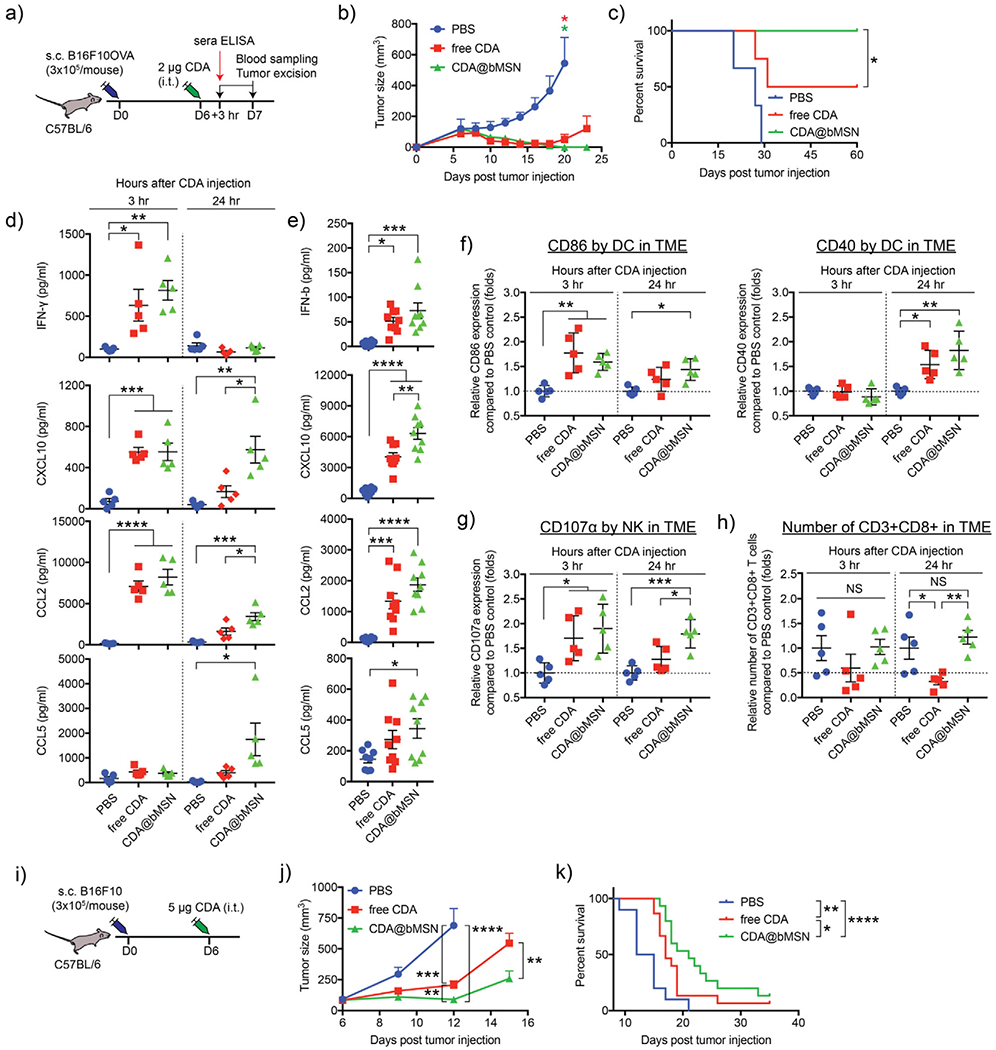
A single intratumoral treatment with CDA@bMSN exerts potent antitumor efficacy. a) C57BL/6 mice were subcutaneously injected with 3 × 105 B16F10OVA cells on the right-side flank. After 6 d, each mouse received intratumoral injection of 2 μg CDA as a soluble or bMSN formulations. After 3 or 24 h, blood sampling and tumor excision were performed. b) Tumor growth curves and c) animal survival are shown. d) Cytokine levels within tumor tissues or e) sera were measured by ELISA after 3 and 24 h or 3 h of CDA injection, respectively. Flow cytometric analyses were performed to examine f) CD86 and CD40 expression on DCs, g) CD107α expression on NK cells, and h) the number of CD8+ T cells within the B16F10OVA TME. i) C57BL/6 mice were subcutaneously injected with 3 × 105 B16F10 cells on the right-side flank. After 6 d, each mouse received intratumoral injection of 5 μg free CDA or CDA@bMSN. j) Tumor growth curves and k) animal survival curves are shown. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, showing representative results from two independent studies with n = 3–4 for (b) and (c) and n = 5 for (d)-(f). n = 15 for (j) and (k) pooled from two independent studies. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 analyzed by one-way or two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD multiple comparison post hoc test. Animal survival curves were analyzed by the log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test.
