Fig. 3.
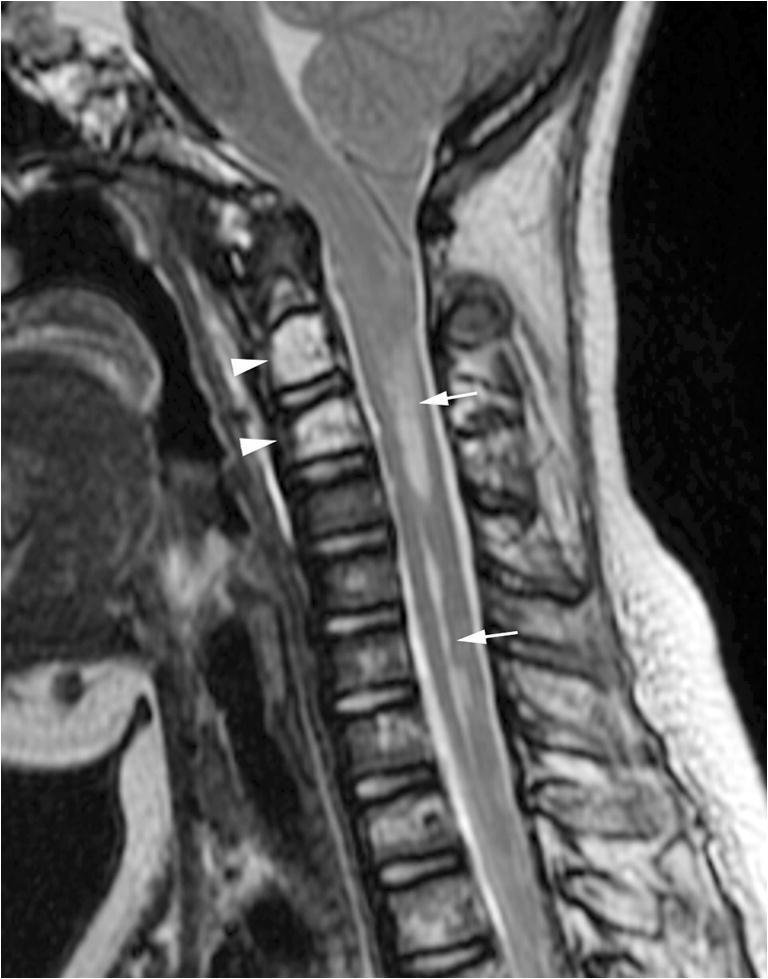
Syrinx secondary to spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Midline sagittal T2-weighted MR image of the spine shows a cervical cord syrinx (arrows) secondary to long-standing cerebellar tonsillar herniation. No extradural spinal collection was identified. Multiple T2 hyperintense lesions in the cervical and upper thoracic spine are consistent with osseous involvement of kaposiform lymphangiomatosis (arrowheads at C2 and C3)
