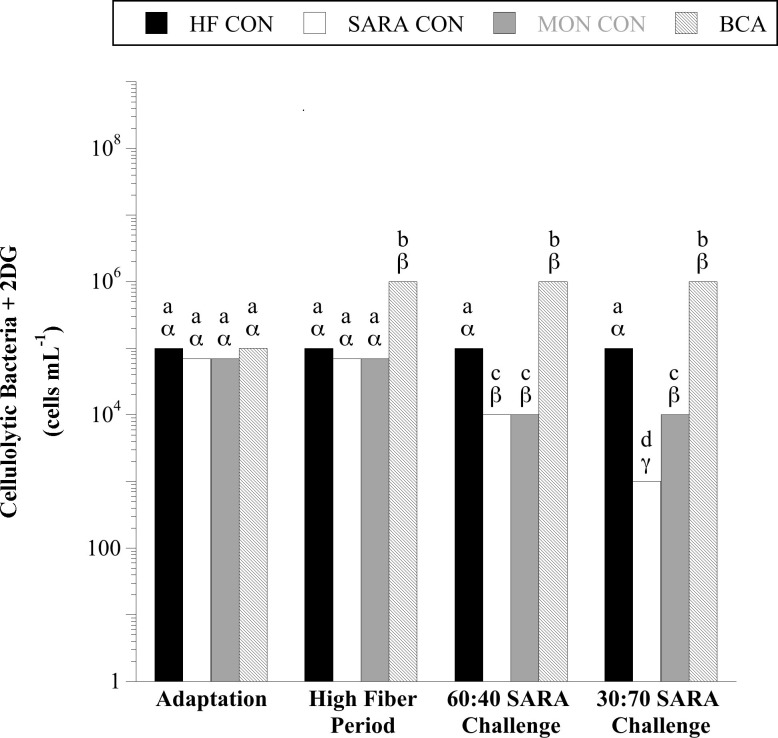
Fig 5. Effect of biochanin A on the viable number of 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) resistant cellulolytic bacteria in rumen fluid (4 h post-feeding).
Holstein steers (n = 12) were blocked by weight into 1 of 4 treatments: High fiber control (HF CON; basal diet control, corn silage + dried distillers’ grain, to meet protein requirements; n = 3), SARA control (SARA CON; n = 3), SARA + monensin treatment (MON CON; 200 mg d-1 monensin; n = 3), or SARA + biochanin A treatment (BCA; 6 g d-1 biochanin A; n = 3). Rumen fluid samples were taken at the end of the adaptation period (100% basal diet), high fiber period (100% basal diet + treatments), 60:40 SARA challenge period (60% basal diet + 40% cracked corn + treatments), and 30:70 SARA challenge period (30% basal diet + 70% cracked corn + treatments) for 2-DG resistant cellulolytic bacterial enumeration. The enumerations were performed in anaerobic liquid media with cellulose (Whatman #1 filter paper strips) as the growth substrate with added 2-DG (6 mmol L-1). The tubes were incubated (39°C, 10 d), and the final dilution exhibiting dissolution of cellulose (visual examination) was recorded as the viable number. Means lacking a common English letter are different within sample day (P < 0.05). Means lacking a common Greek letter are different over sample days within treatment (P < 0.05). Treatment: P < 0.0001, sample day: P < 0.0001, and treatment × sample day: P < 0.0001; Pooled SEM: Treatment = 0.1273, sample day = 0.0867, treatment × sample day = 0.1735 (log transformed).