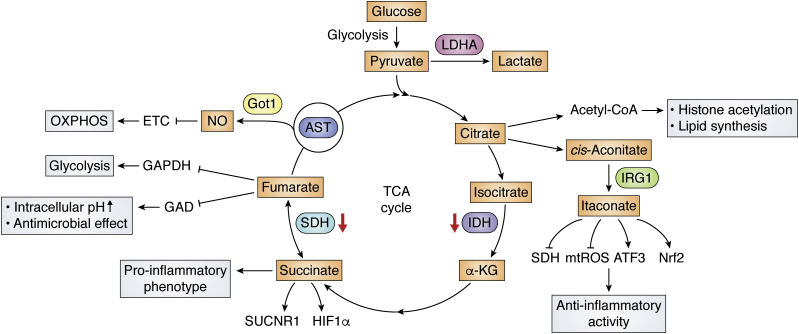
Figure 1.
The effect of TCA intermediates on macrophage activation. Proinflammatory macrophages exhibit two breaks in the TCA cycle (at IDH and SDH), leading to the accumulation of citrate and succinate, and induction of the arginine-succinate shunt (AST) to support NO production. Itaconate, produced by the enzyme immune-responsive gene 1 (IRG1), exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the activity of SDH and stimulating Nrf2 and activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) induction. Fumarate, another TCA metabolite, is highly antimicrobial toward L. monocytogenes under acidic conditions by inhibiting the GAD (glutamic acid decarboxylase) system, which results in intracellular pH increase. It also has an inhibitory effect on aerobic glycolysis by suppressing GAPDH activity.