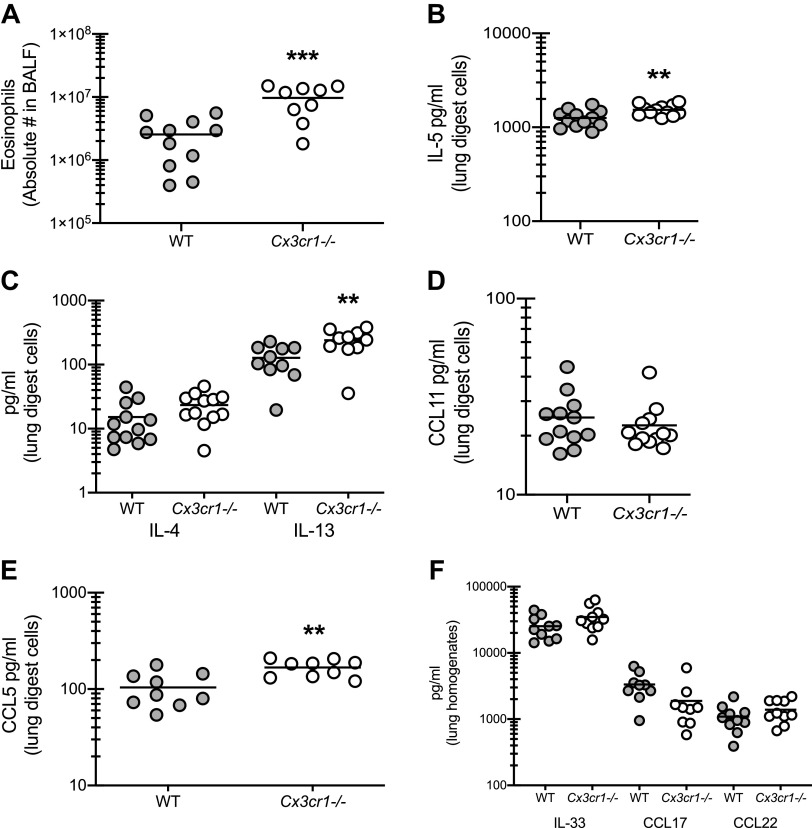
Figure 4.
CX3CR1 signaling regulates the magnitude of type 2 responses during fungal-associated allergic airway inflammation. A: C57BL/6 [wild-type (WT)] and CX3CR1-deficient (Cx3cr1-/-) mice were chronically exposed to Aspergillus fumigatus as described in materials and methods. Twenty-four hours after the last organism challenge, lung cells were isolated by bronchoalveolar lavage, enumerated, Fc-blocked, stained with a live/dead staining kit, and stained for eosinophils (CD45+, CD11b+, Siglec F+, Ly-6G−). A illustrates cumulative data from 3–4 independent studies (n = 3–4 mice per group per study). B–E: 24 h after last challenge, right lungs were collected and enzymatically digested and unfractionated lung cells were cocultured with A. fumigatus conidia for 24 h at a cell to organism ratio of 1:1. IL-5 (B), IL-4 and IL-13 (C), CCL11 (D), and CCL5 (E) levels were quantified in lung digest cell culture supernatants by Milliplex. F: 24 h after last challenge, the left lungs were collected and homogenized and IL-33, CCL17, and CCL22 levels were quantified in clarified lung homogenates. B–E illustrate cumulative data from 2–3 independent studies (n = 3–5 mice per group per study). **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 (two-tailed Student’s t test).