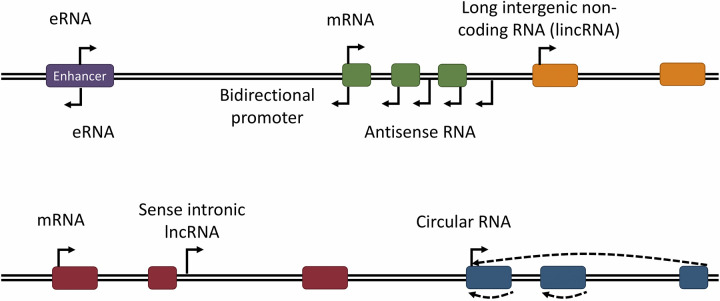
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of abundant long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) subtypes based on their transcriptional origin in the genome. Although long intergenic noncoding RNAs (lincRNAs) are transcribed from an independent noncoding gene, many lncRNAs are not. eRNAs are transcribed from enhancer sequences, frequently from bidirectional promoters in these DNA elements. Antisense RNAs overlap 1 or more genes in the opposite orientation and often originate from bidirectional promoters as well. Additional lncRNAs are transcribed from intronic sequences (sense intronic lncRNAs) or 3′-untranslated regions (UTRs). Circular RNAs are typically transcribed from protein-coding genes but undergo backsplicing to generate a circular transcript that may contain intronic, exonic, or both intronic and exonic sequences.