Figure 4.
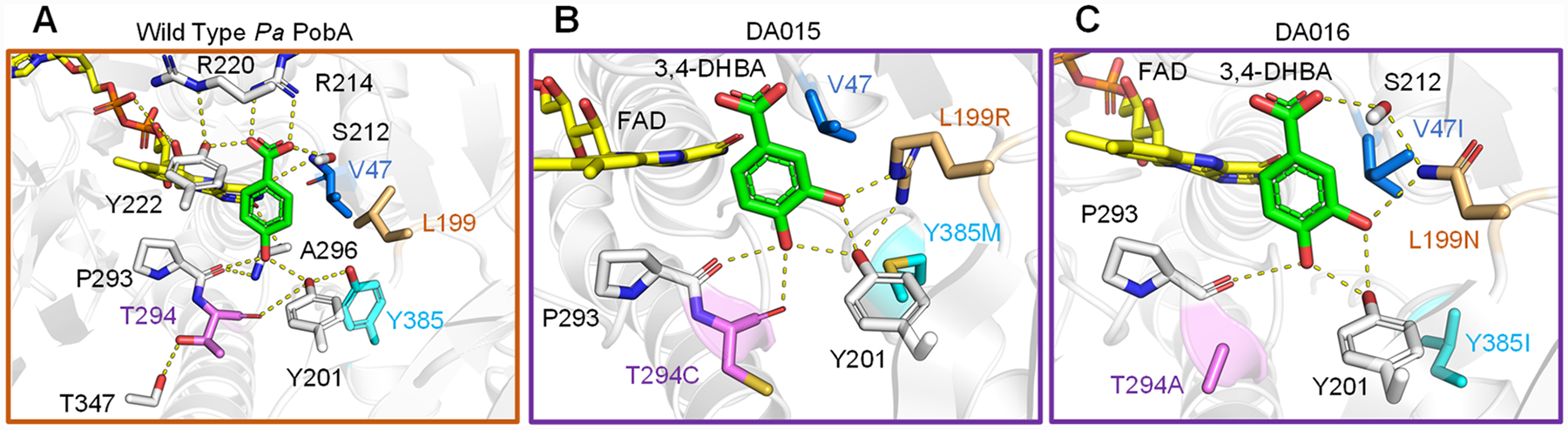
4-HBA and 3,4-DHBA binding poses. (A) In wild-type PobA (PDB: 1IUW), the productive binding mode is described by the hydrogen-bonding networks stabilizing 4-HBA and positioning the 3-carbon toward FAD for hydroxylation. (B) In the DA015 model, L199R supports Y201 and forms a new contact to the ligand 3-hydroxyl. Y385M makes space, no substitution occurs at V47, which maintains close hydrophobic packing against L199R, and T294C loosens the helix for increased flexibility and improved backbone hydrogen bonding to the 4-hydroxyl. (C) In the DA016 model, L199N forms interactions stabilizing S212 and to the ligand 3-hydroxyl. Y385I creates space, V47I braces L199N to minimize side-chain mobility, and T294A allows P293 to move closer to 3,4-DHBA. Importantly, the mutations orient 3,4-DHBA such that the 5-carbon is optimally exposed to FAD for hydroxylation in both variants. Detailed methods of Rosetta modeling are included in the Supporting Information.
