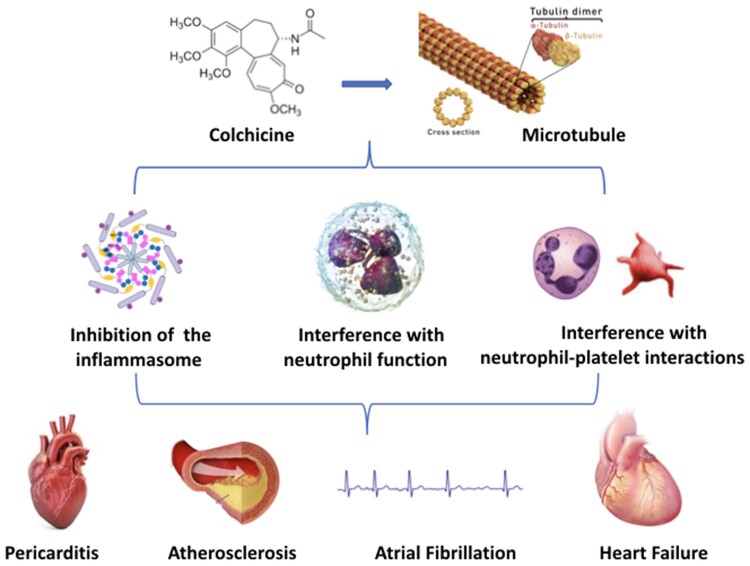
The central mechanism of the anti-inflammatory action of colchicine is the inhibition of microtubule function leading to the inhibition of granulocyte function, interference with selectin expression and neutrophil–platelet interactions, and non-specific inhibition of the assembly of the inflammasome in inflammatory cells. These actions could exert therapeutic effects in different cardiovascular diseases (e.g. pericarditis, acute and chronic coronary syndromes, atrial fibrillation, and heart failure).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.