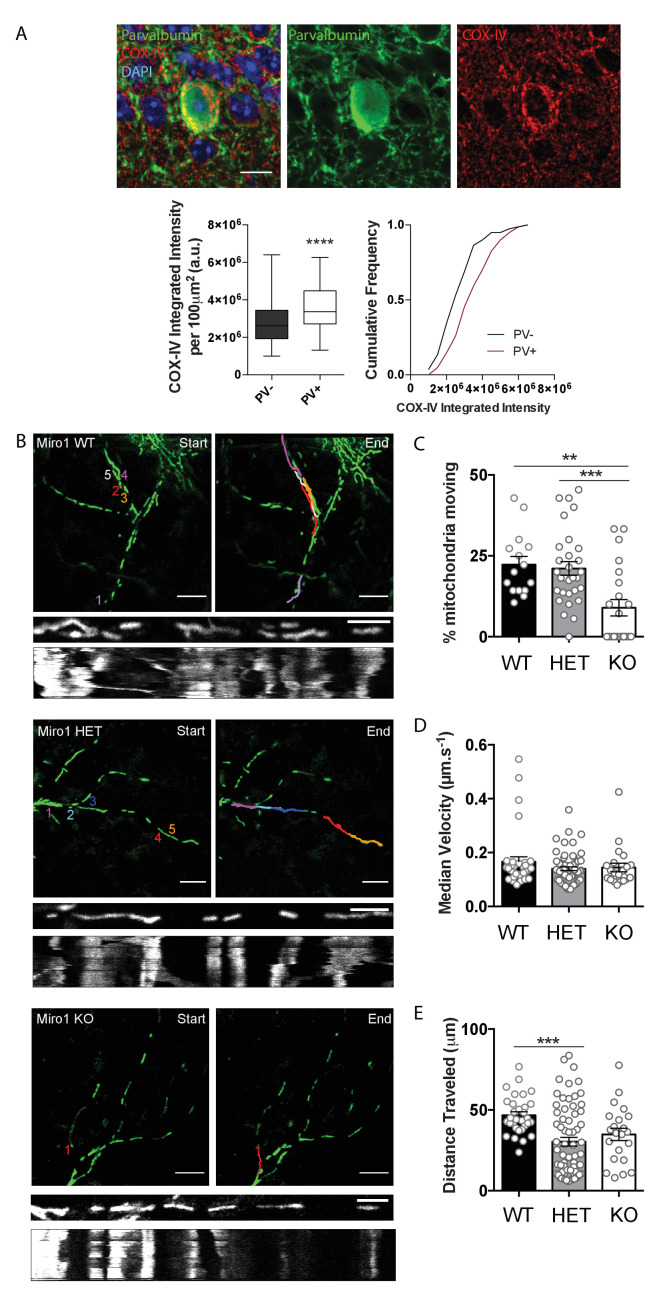
Figure 1. Cell-type specific removal of Miro1 from parvalbumin interneurons impairs mitochondrial trafficking.
(A) COX-IV levels in PV+ interneurons. The fluorescence signal of COX-IV is increased in PV immuno-positive cells in the hippocampus. Scale bar = 10 μm. Boxplot and cumulative distribution show the quantification of the mean integrated intensity of the COX-IV fluorescent signal in PV immuno-positive and -negative regions (n = 81 cells, 11 slices, three animals). (B) Miro1-directed mitochondrial trafficking in organotypic brain slices. Representative images from a 500 s two-photon movie of MitoDendra+ mitochondria in PV+ interneurons in ex vivo organotypic hippocampal slices from WT, ΗΕT, and Miro1 KO animals. The colored numbers/lines denote tracks of individual mobile mitochondria during the movie. Scale bar = 10 μm. The kymographs represent the mitochondrial displacement over time. Scale bar = 5 μm. (C) Quantification of the percentage of moving mitochondria (nWT = 15 movies, nine slices, four animals, nΗΕT = 32 movies, 10 slices, four animals, nKO = 22 movies, eight slices, four animals). (D) Quantification of the median velocity (nWT = 35 mitochondria, nΗΕT = 65 mitochondria, nKO = 22 mitochondria). (E) Quantification of the distance traveled (nWT = 31 mitochondria, nΗΕT = 66 mitochondria, nKO = 22 mitochondria).