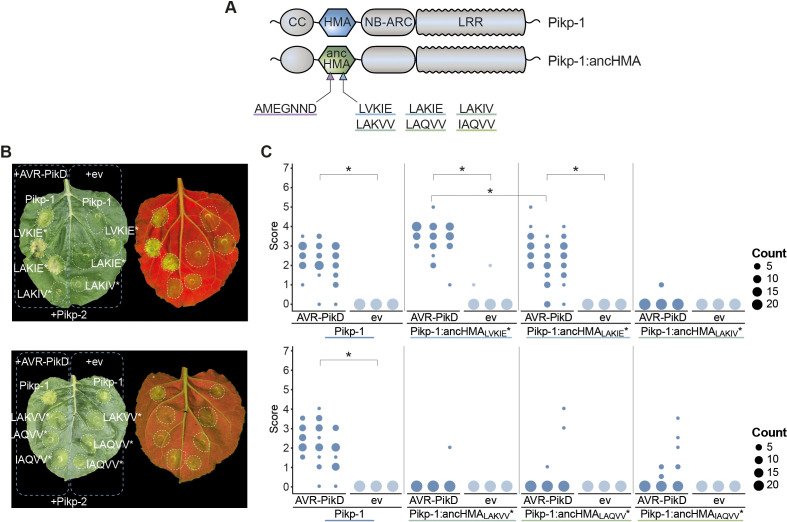
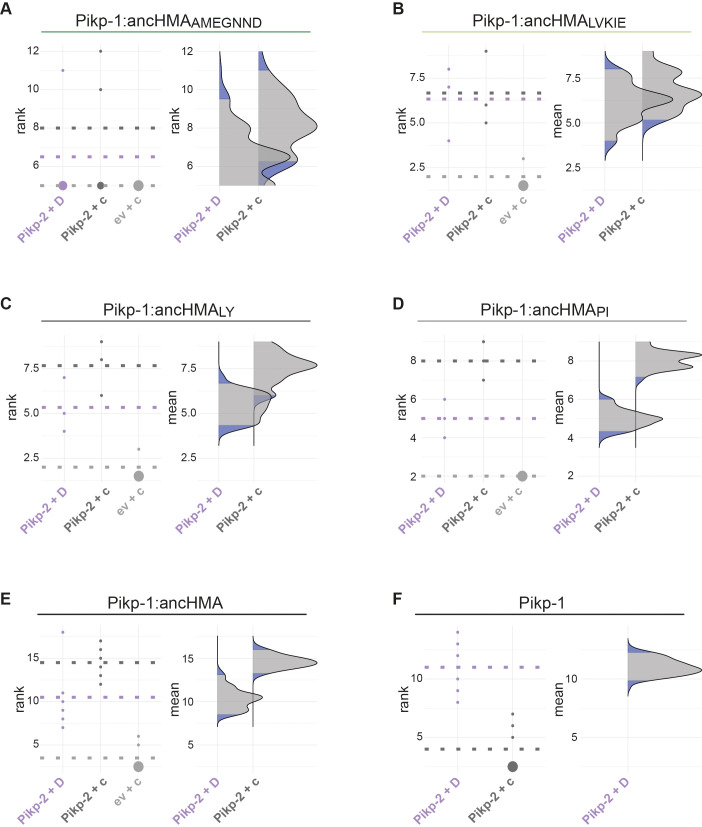
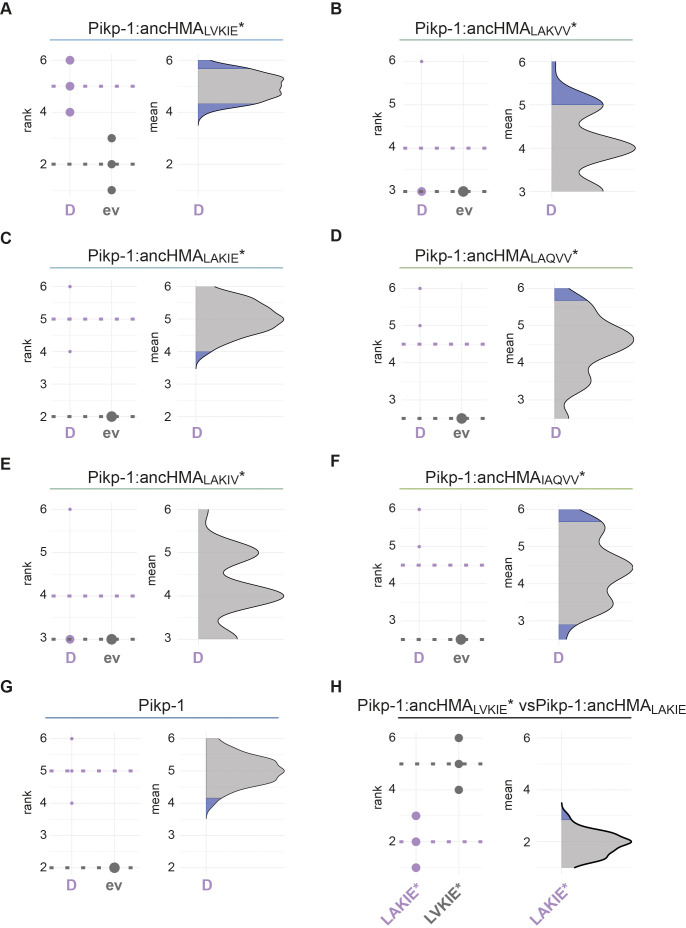
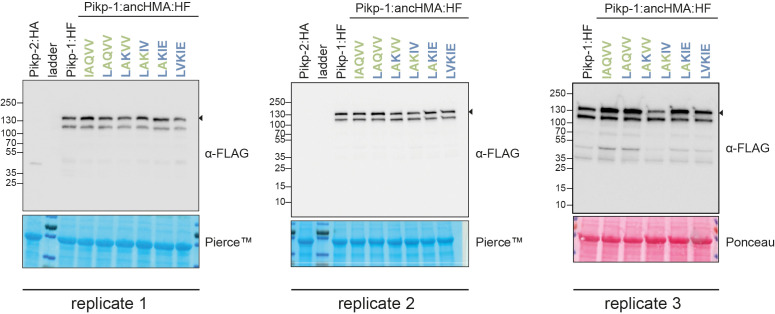
Figure 6. Pikp-1:ancHMALVKIE* and Pikp-1:ancHMALAKIE* mediate immune response towards the AVR-PikD effector.
(A) Schematic representation of wild-type Pikp-1 and Pikp-1:ancHMA fusions used in the assay. The mutated regions are presented with arrowheads and listed. (B) Representative images of hypersensitive response (HR) cell death assay after transient co-expression of the Pikp-1:ancHMA* mutants (C-terminally tagged with HF) with AVR-PikD (N-terminally tagged with Myc) and Pikp-2 (C-terminally tagged with HA). Empty vector (ev) was used as a negative control. All constructs were co-expressed with the gene silencing suppressor p19 (Win and Kamoun, 2003). The leaves were photographed 5 days after infiltration under daylight (left) and UV light (right). (C) HR was scored at 5 days post-agroinfiltration. The results are presented as dot plots, where the size of a dot is proportional to the number of samples with the same score (count) within the same biological replicate. The experiment was independently repeated at least three times with 23–24 internal replicates; the columns within tested conditions (labelled on the bottom) correspond to results from different biological replicates. Significant differences between relevant conditions are marked with an asterisk (*); details of the statistical analysis are summarised in Figure 6—figure supplement 5.