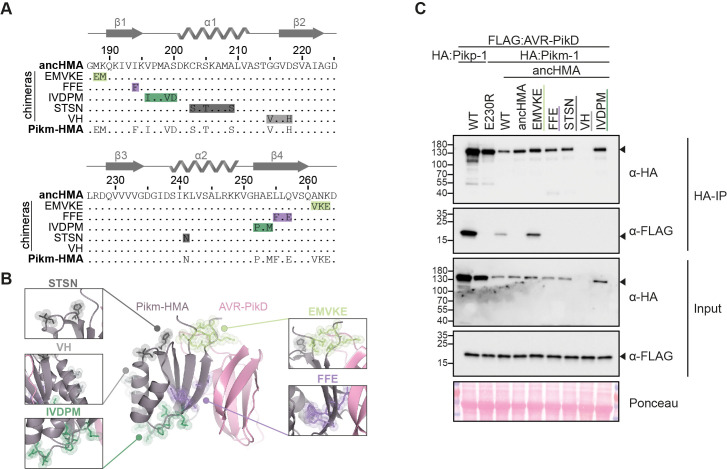
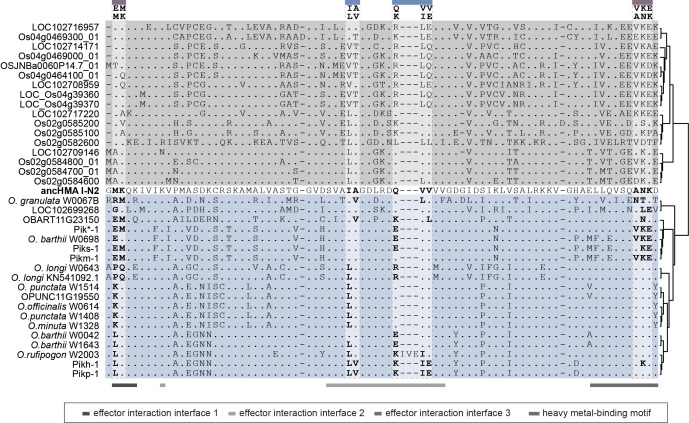
Figure 7. The MKANK/EMVKE region of the heavy metal-associated (HMA) domain of Pikm-1 determines high-affinity AVR-PikD binding.
(A) Protein sequence alignment between the ancestral HMA (ancHMA), Pikm-HMA, and Pikm–ancHMA chimeras. The protein model above the alignment depicts Pikm-HMA secondary structure. The colour-coded rectangles mark polymorphic regions used for chimeric swaps. (B) Schematic representation of the Pikm-HMA domain (purple) in complex with AVR-PikD (pink) (De la Concepcion et al., 2018), with polymorphic regions between Pikm-HMA and ancHMA colour-coded as in (A). The molecular surfaces of the polymorphic residues are also shown. (C) EMVKE substitutions in the ancHMA restore in planta association with AVR-PikD. Co-immunoprecipitation experiment between AVR-PikD (N-terminally tagged with FLAG) and Pikp-1:ancHMA chimeras (N-terminally tagged with FLAG), labelled above. Wild-type (WT) Pikp-1/Pikm-1 and Pikp-1E230R were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. Immunoprecipitates (HA-IP) obtained with anti-HA probe and total protein extracts (input) were immunoblotted with the appropriate antisera (labelled on the right). Rubisco loading control was carried out using Ponceau staining. Arrowheads indicate expected band sizes. Three independent replicates of this experiment are shown in Figure 7—figure supplement 2.