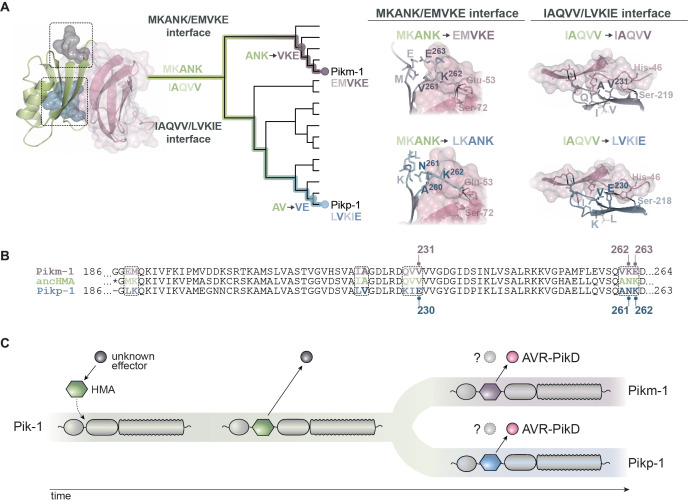
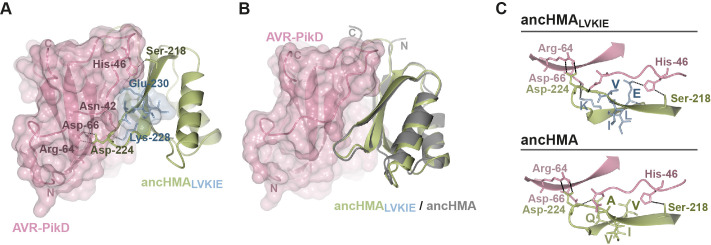
Figure 9. Model of molecular convergence of Pikp-1 and Pikm-1 towards AVR-PikD binding at high affinity.
(A) The heavy metal-associated (HMA) domains of Pikp-1 and Pikm-1 receptors have convergently evolved through distinct evolutionary and biochemical paths to bind AVR-PikD with high affinity. The Pikp-HMA domain evolved through the AV-VE adaptations in the IAQVV/LVKIE region, whereas Pikm-HMA domain acquired the ANK-VKE mutations in the MKANK/EMVKE region. Schematic representations of the HMA–AVR-PikD structures, adapted from De la Concepcion et al., 2018, are presented with selected side chains shown as sticks and labelled; the colours of the residue labels match colours of the respective molecules. Dashed lines stand for hydrogen bonds or salt bridges. (B) The protein sequence alignment between Pikp-HMA, Pikm-HMA, and ancestral HMA (ancHMA), with relevant amino acids marked. (C) We propose a model in which the HMA effector target integrated into Pik-1 to bait the recognition of an unknown effector. Throughout evolution the Pik-1 receptor and its integrated HMA domain diversified and led to the emergence of the Pikp-1 and Pikm-1 allelic variants that bind newly emerged AVR-PikD effector.