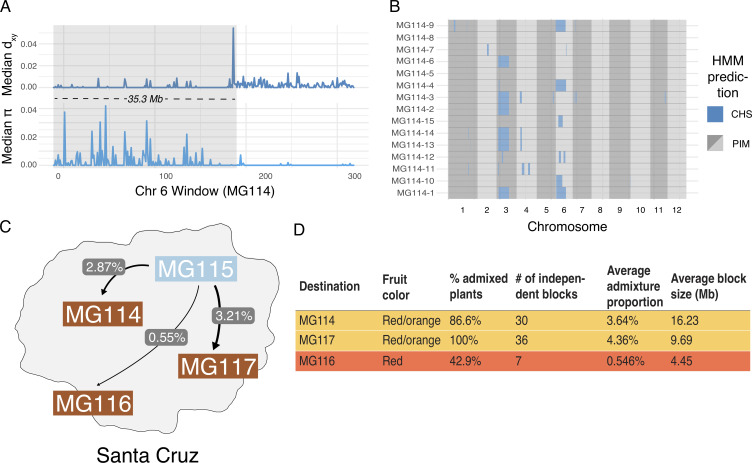
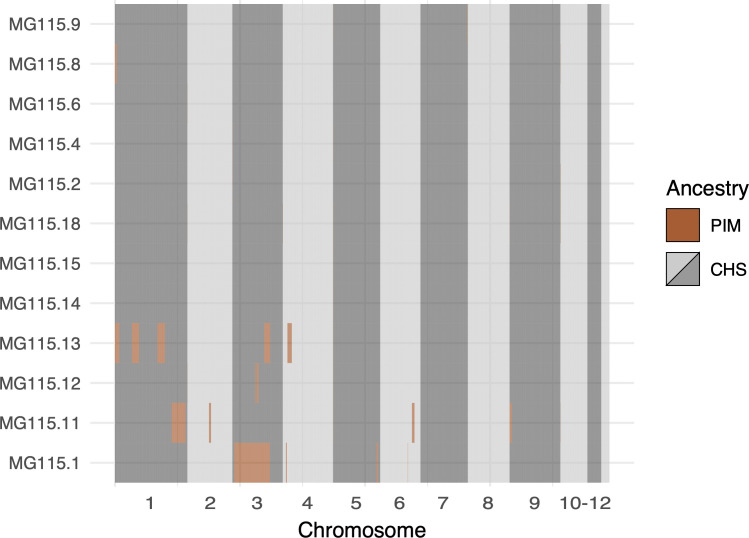
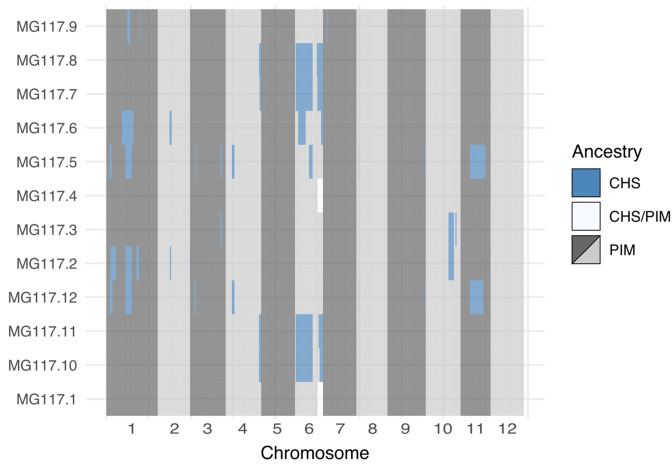
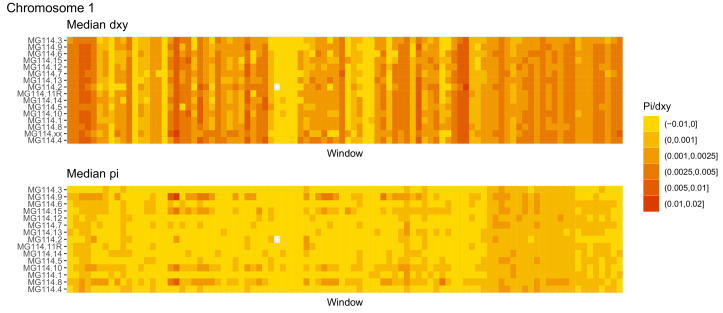
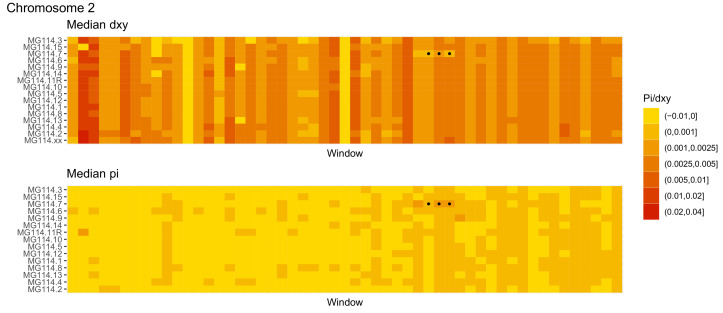
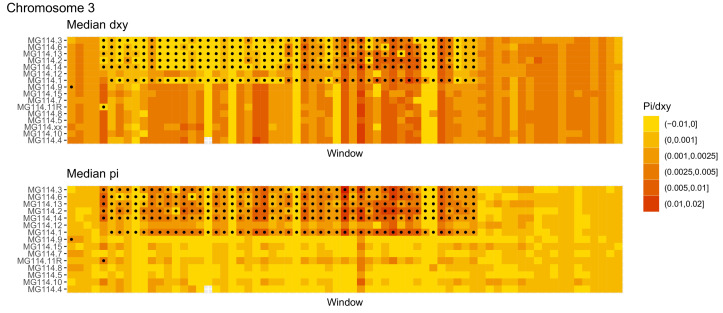
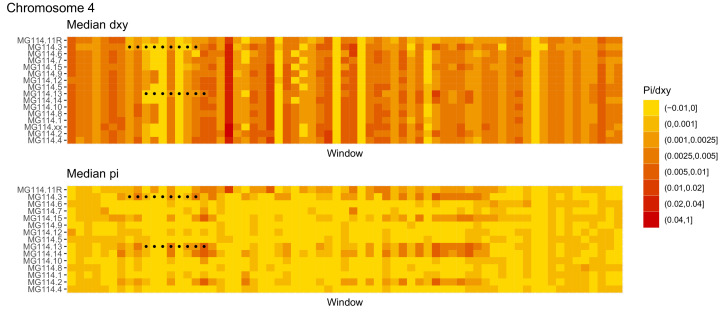
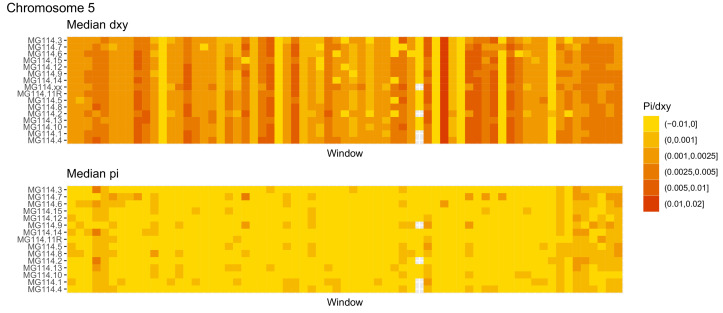
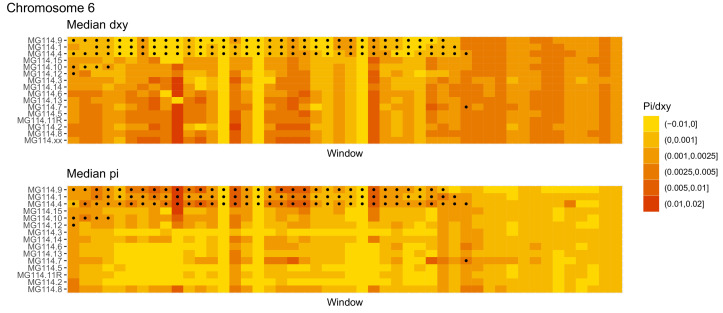
Figure 4. Local ancestry assignment using hidden Markov model (HMM) characterizes a history of endemic × invasive introgression.
(A) Patterns of diversity and divergence along chromosome 6 for an MG114 individual. The region of recent coalescence (low divergence; high diversity) with CHS is annotated in gray. This 20.2 kb block segregates at 20% in MG114. (B) Genome-wide HMM predictions for all individuals in MG114. The x-axis is ordered by chromosome and y-axis is ordered by individual. Two large CHS haplotypes segregate at high frequency on chromosomes 3 (40%) and 6 (20%). (C) Visual summary of admixture proportions from CHS into three PIM populations. (D) Summary of HMM assignment for each PIM population. Populations displaying variation in fruit color (MG114 and MG117) have more CHS ancestry than those which are fixed for the ancestral red state (MG116).