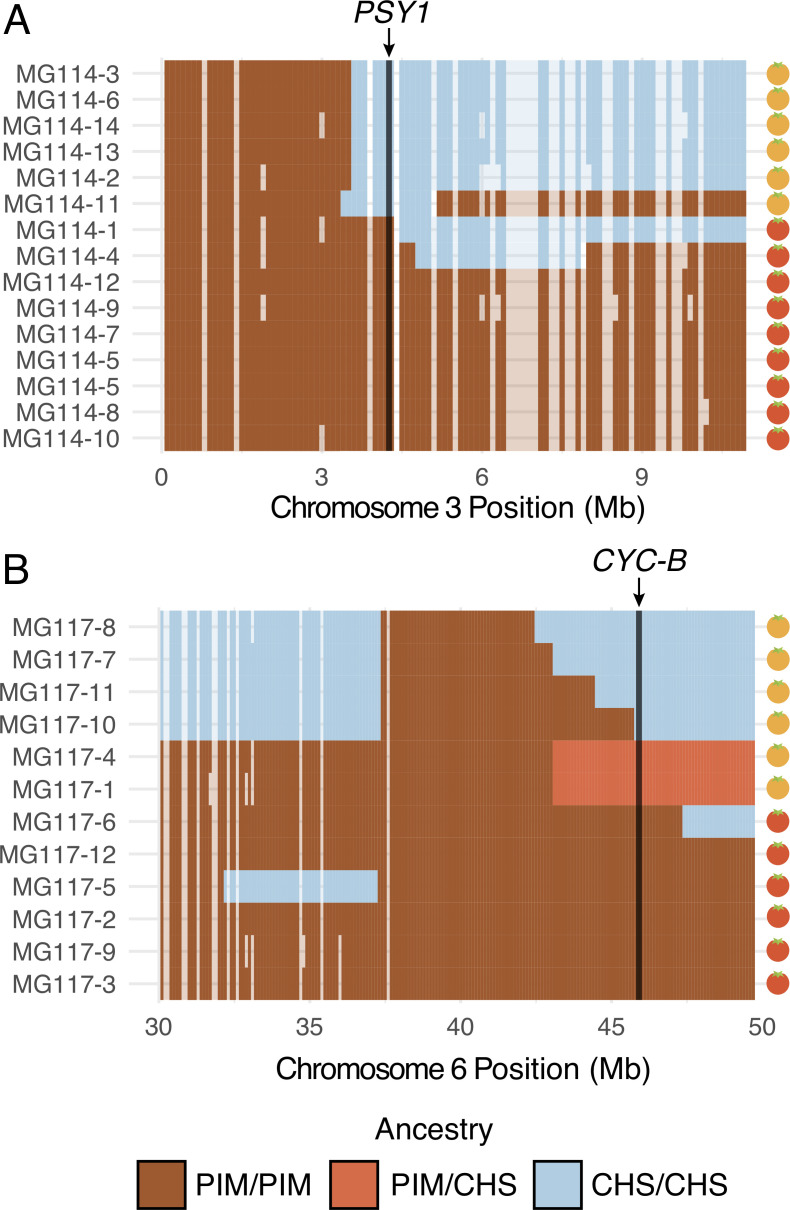
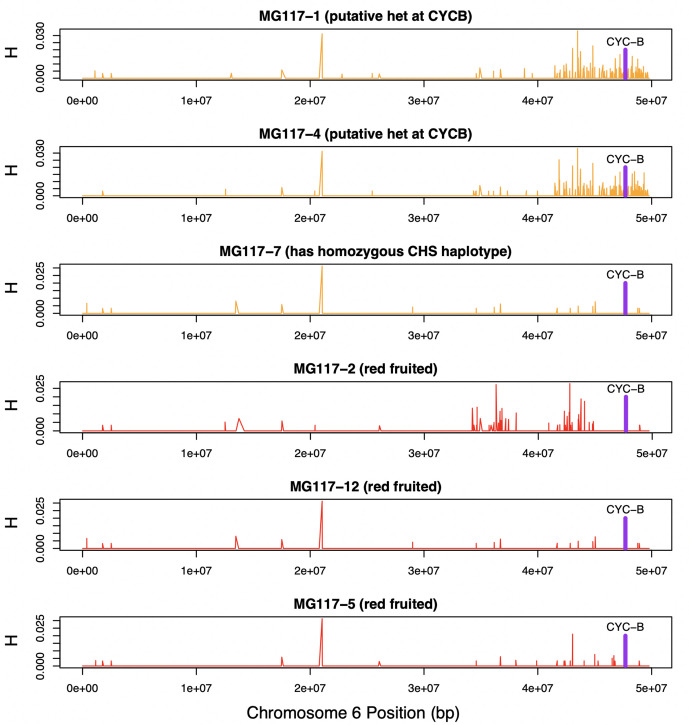
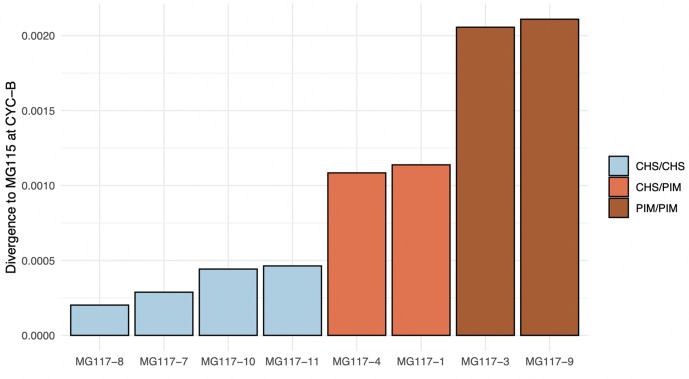
Figure 5. Patterns of local ancestry across focal chromosome regions of MG114 and MG117, enlarged to show variation in introgression block break points at color pathway genes.
(A) CHS ancestry at carotenoid biosynthesis gene PSY1 on chromosome 3 correlates with observed fruit color variation in MG114. (B) CHS ancestry at carotenoid biosynthesis gene CYC-B on chromosome 6 correlates with fruit color variation in MG117. Each cell represents 100 kb. Empty cells indicate windows with no sequence data. Empty cells are ghost shaded with each ancestry color based on neighboring assignments.