Scheme 2.
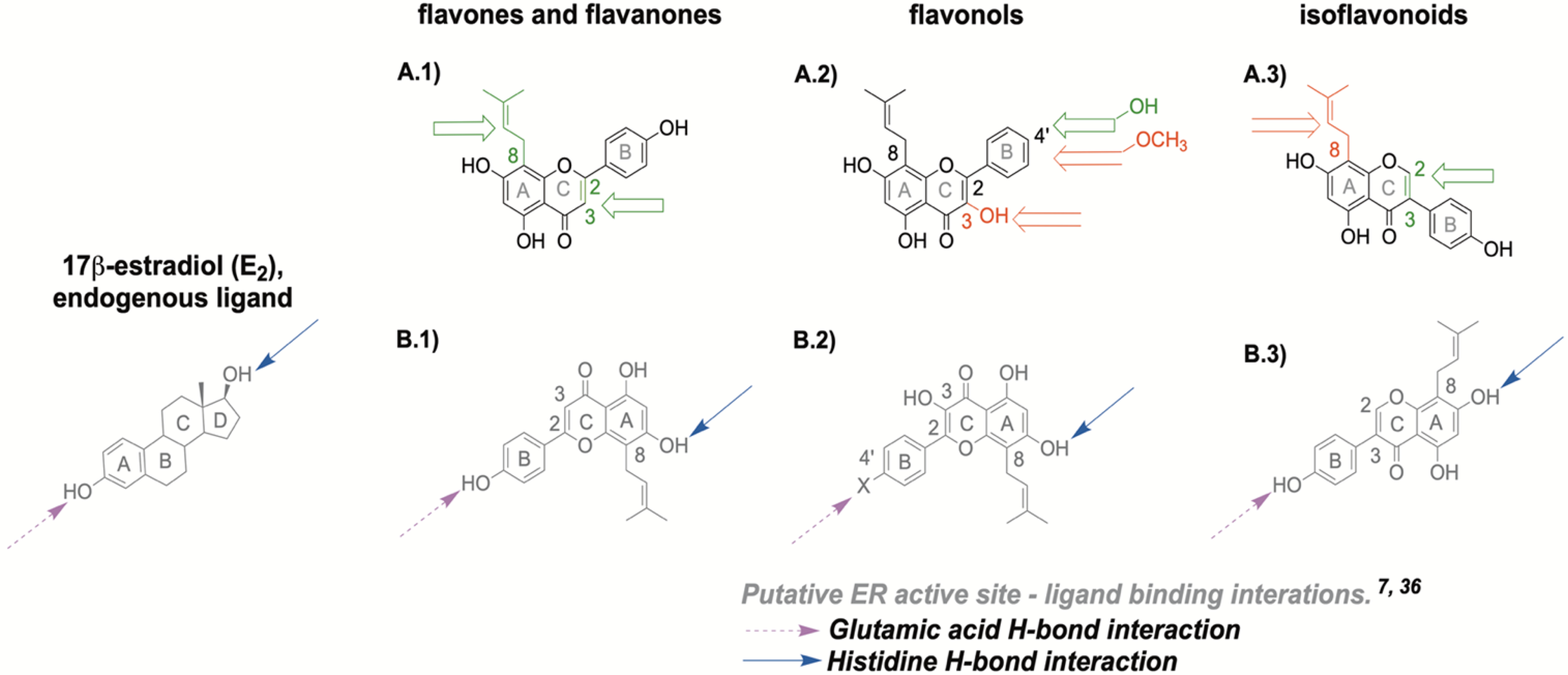
Tested flavonoid structures with putative ER binding interactions: (A.1) flavanone and flavone structure with A-ring prenylation at 8 position (C8) and (un)saturation at C2-C3. (A.2) flavonol structure with C3 hydroxyl group and B-4’ position for hydroxyl or methoxy group (A.3) isoflavonoid structure with C8 prenylation and (un)saturation at C2-C3. The open green arrow represents an increased ERβ activity when the considered substitution is present on the core flavonoid structure, whereas the open red arrow indicated a decreased activity. (B.1) ER binding interactions of flavanones and flavones, (B.2) of flavonols, (B.3) of isoflavonoids in relation to E2. Blue full-tailed arrows represent moieties with hydrogen bond (H-bond) interactions with histidine residue in the ER binding site; magenta dash-tailed arrows represent moieties with H-bond interactions with glutamic acid residues in ER binding site.
