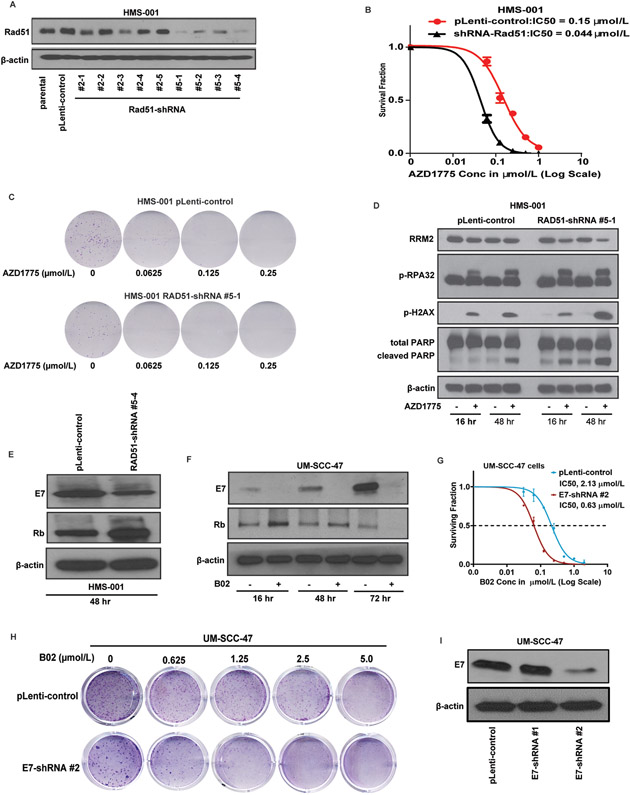
Figure 2. Rad51 knockdown induces DNA damage and replication stress responses and apoptosis in HNSCC cells treated with Wee1 kinase inhibitor.
HPV-positive HNSCC (HMS-001) cells were stably transfected with pLenti-viral vector control or Rad51 shRNA plasmids and protein lysates were prepared as described in Methods. A, Western blot analyses showing successful knockdown clones of Rad51 (clones #5-1 and #5-4). Lysate from HMS-001 parental cells was used as positive control. B, clonogenic survival assay showing sensitivity of HMS-001 cells expressing Rad51-shRNA clone #5-1 to AZD1775 treatment. Data points represent the mean ± SEM of triplicate experiments. C, representative images of clonogenic survival assays for HMS-001 with pLenti-viral vector control and Rad51 shRNA clone#5-1 respectively. The HMS-001 cells with control vector and Rad51-shRNA #5-1 were then treated with/without AZD1775 for 16 and/or 48 hours and subjected to immunoblot analysis using antibodies as indicated. D, increased levels of phosphorylation of markers of DNA damage (p-γH2AX (S134), replication stress (pRPA32) responses, and decreased total levels of ribonucleotide reductase M2 (RRM2). PARP1 cleavage indicates induction of apoptosis in these cells. E, Rad51 knockdown inhibits E7 and enhances expression levels of Rb in HMS-001 cells. F, inhibition of E7 and enhanced Rb protein levels in UM-SCC-47 cells treated with 10 μmol/L B02 at various time point. G and H, clonogenic survival plot and representative clonogenic images showing increased sensitivity of UM-SCC-47 cells expressing E7-shRNA plasmid to treatment with B02 respectively. Knockdown of E7 was confirmed by immunoblotting (I). The β-actin served as loading control.