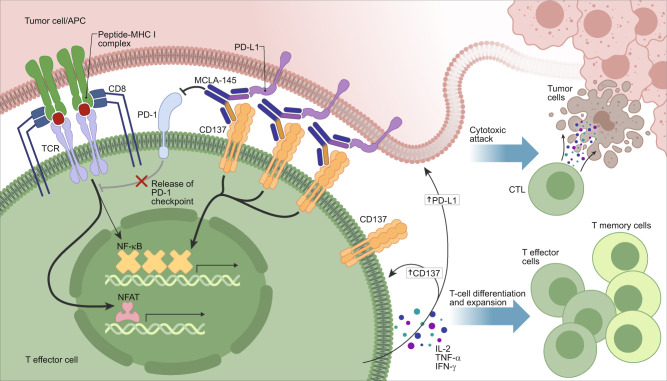
Fig. 7. Schematic of the MCLA-145 mechanism of action.
MCLA-145 is shown binding to PD-L1 expressed on a tumor cell or APC (depicted in pink) and CD137 expressed on a T effector cell (depicted in green). Engagement of MCLA-145 results in clustering of CD137 molecules on the surface of the effector T cell and downstream activation of the NF-kB signaling pathway. In addition, engagement of PD-L1 by MCLA-145 blocks interaction with its receptor PD-1 reversing PD-1 dependent suppression of downstream signaling from the T cell receptor complex. The net effect of MCLA-145 binding in trans to tumor cell/APC and T effector cells is shown: upregulation of CD137 (on T cells) and PD-L1 (on tumor cells and APCs), the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines from effector T cells resulting in T cell differentiation and expansion and activation of effector T cells to promote cytotoxic attack of tumor cells.