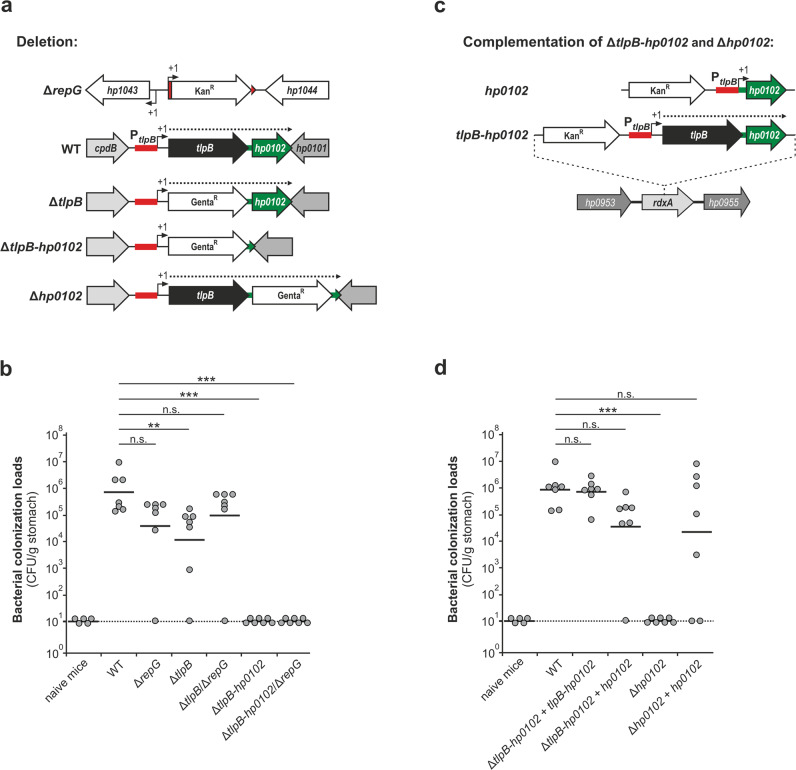
Fig. 3. HP0102 is essential for mice stomach colonization with H. pylori strain X47-2AL.
a, c Schematic representation of the construction of H. pylori X47-2AL ∆repG and ∆tlpB/hp0102 deletion mutant and complementation strains. TSS are denoted as +1 (black arrows). The repG gene and the tlpB promoter (PtlpB) are shown in red. The hp0102 gene is shown in green. b, d About 108 bacteria of H. pylori X47-2AL WT or indicated mutant strains were orogastrically administered to NMRI Swiss mice. As a control, mice were infected with peptone broth only. Four weeks post infection, mice were sacrificed and colony-forming units (CFUs) per gram of stomach weight were calculated by serial dilutions and plating assays. Each circle indicates the colonization titer in the stomach of a single mouse. The horizontal bars represent the geometric mean for each group of data (n = 5/4 non-infected control animals for panel b/d, respectively; n = 7 for mice infected with indicated H. pylori strains). ***—highly significant, p-value < 0.001; **—very significant, p-value < 0.01; n.s.—not significant; Mann–Whitney test (Prism), two-tailed. Source data underlying (b, d) are provided as a Source data file.