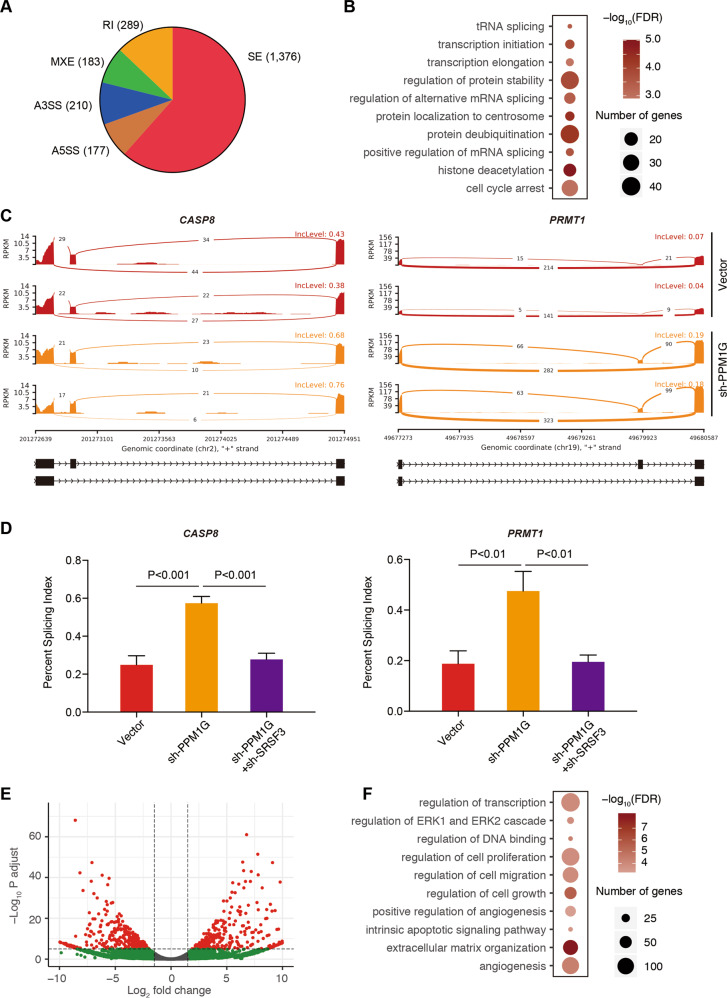
Fig. 6. PPM1G regulated the alternative splicing in HCC.
A–B Identify PPM1G-related alternative splicing events. Alternative splicing analysis was conducted in Hep3B cells with and without PPM1G knockdown. The pie plot shows the distribution of the alternative splicing events (A). A gene ontology analysis of differentially alternative splicing events in Hep3B cells with PPM1G knockdown was completed (B). C This illustration represents alternative splicing events of the CASP8 gene and PRMT1 gene. The reads at the junction site between two exons were plotted. The red color represents the RNA-seq of vector-transduced Hep3B cells, and the orange color represents the RNA-seq of sh-PPM1G-transduced Hep3B cells. D PPM1G’s alternative splicing regulation was achieved by SRSF3. The alternative splicing at the CASP8 and PRMT1 in Hep3B cells transfected with shRNA targeting the PPM1G, PPM1G + SRSR3, or vector were examined by real-time RT-qPCR. E–F The differential expressed genes (DEG) post-PPM1G knockdown were identified. DEGs were obtained by RNA-seq analyses of cells transfected with shRNA-targeting PPM1G or vector. The volcano plot was shown (E). Gene ontology analyses of the DEGs were plotted (F).