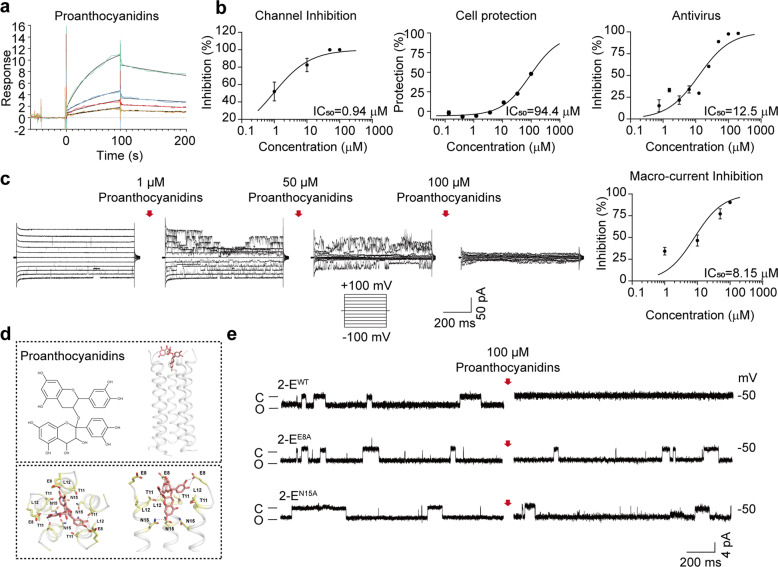
Fig. 3. The interaction mechanism of proanthocyanidins with the 2-E channel.
a Binding ability of proanthocyanidins, wortmannin, and veliparib to 2-E channel via SPR. b IC50 of proanthocyanidins on cell protection, channel inhibition, and antivirus. c Proanthocyanidins inhibited 2-E-induced macro-currents. Left, proanthocyanidins dose-dependently inhibited 2-E-induced macro-current. Right, IC50 of proanthocyanidins on macro-currents inhibition (n = 3). d A representative docking pose of proanthocyanidins. The protein was shown in cartoon depict. The compound and key residues are shown as sticks. The putative hydrogen bonds are shown as dash lines. e Representative single-channel traces after the indicated 2-E mutant channels exposed to 100 μM proanthocyanidins at −50 mV. Once ion channel conductance was detected, compounds were added to the trans side while stirring to facilitate binding of the compound to the channel. The red arrow indicates the application of compounds (n ≥ 3). “C” means channel close; “O” means channel open.