FIGURE 1.
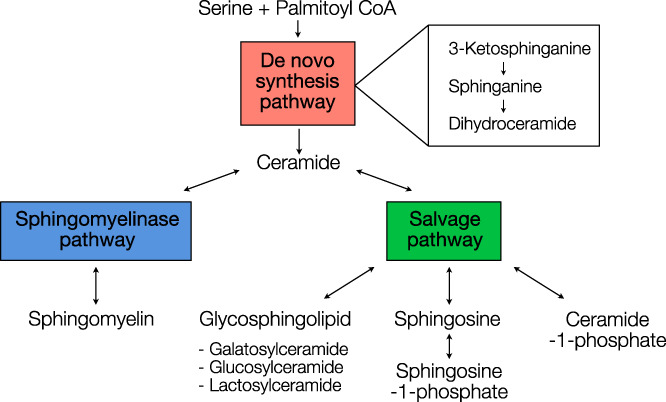
An overview of sphingolipid metabolic pathways, according to Merrill 11 and Maceyka and Spiegel. 2 The synthesis of ceramide begins with the condensation reaction of serine and palmitoyl‐CoA to form 3‐ketosphinganine. Along the de novo synthesis pathway (red), 3‐ketosphinganine is reduced to sphinganine. Sphinganine is coupled with fatty acyl‐CoA to form dihydroceramide, and a double bond is added on dihydroceramide to form ceramide. Ceramide is the central hub of the sphingolipid metabolism, which can be modified into sphingomyelin through the sphingomyelinase pathway (blue) and can be modified into glycosphingolipids or phosphorated sphingolipids through the salvage pathway (green). Double‐headed arrows indicate a reversible reaction
