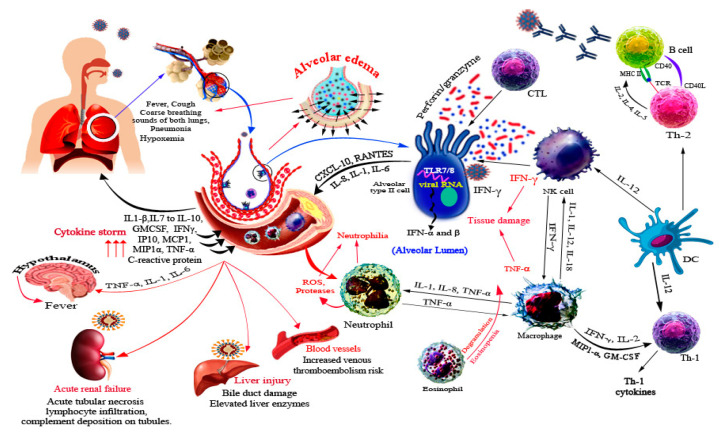
Figure 3.
Immune response and immunopathogenesis associated with SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 infects mainly type II alveolar cells and upon infection a wide array of cytokines and chemokines is secreted, which recruits several immune innate cells. Recruitment of cells further potentiates the immune response and usually results in tissue damage due to high concentration of IFN-γ and TNF-α. In addition, degranulation of eosinophils, proteases and ROS of neutrophils cause tissue damage. The participation of immune response in disease progression is illustrated by red arrows. SARS-CoV-2 is reported to cause systemic infections of liver, kidneys, and blood vessels.