Figure 5.
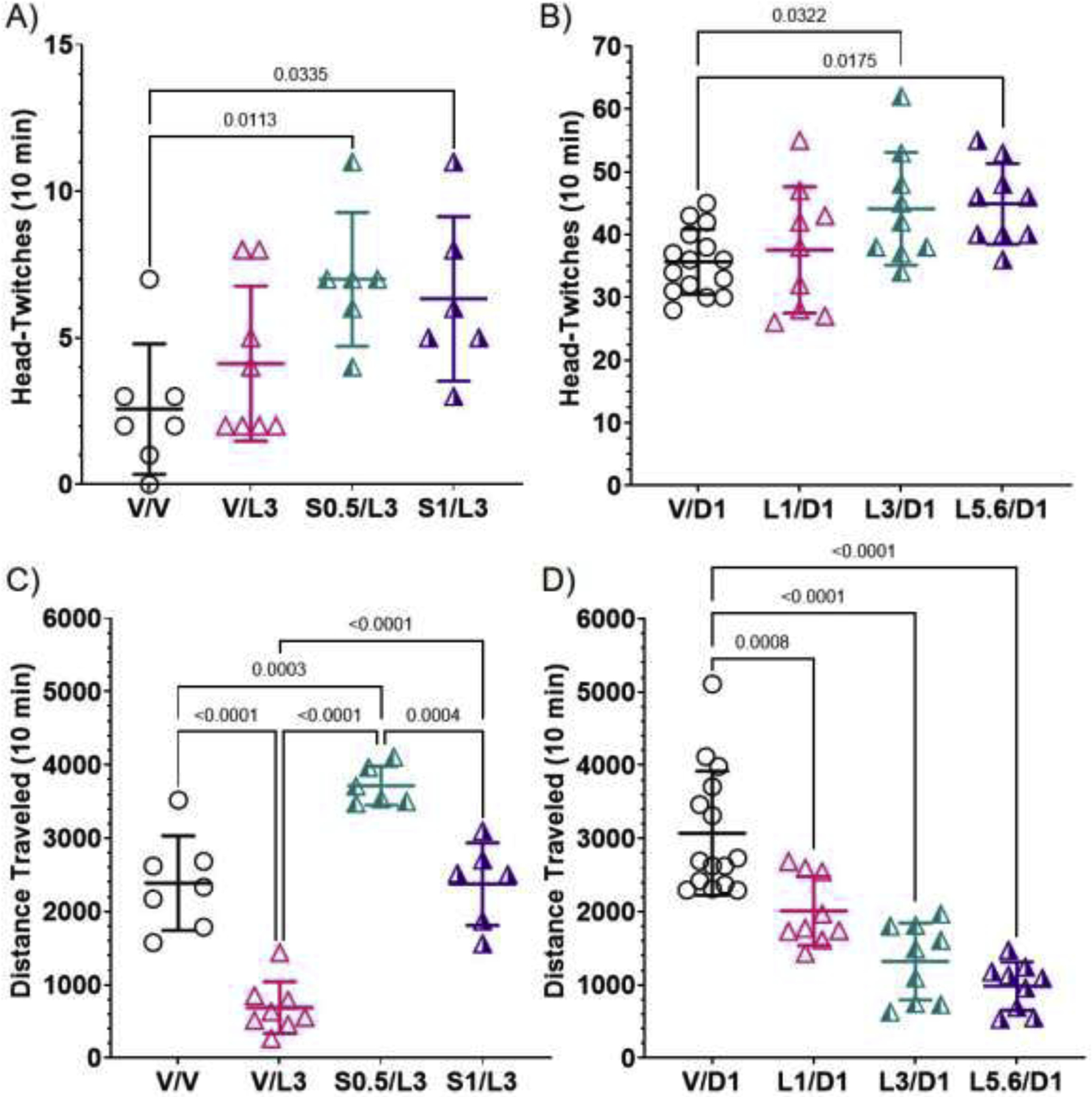
Effects of lorcaserin on the 5-HT2AR-dependent HTR (A and B) and on locomotion (C and D), sensitive to 5-HT2CR activation in C57BL/6J mice. Lines through data points represent means and SDs. A) Lorcaserin at 3 mg/kg (V/L3) did not elicit more HTRs than vehicle-treated (V/V) C57BL/6J mice, however, when co-administered with 0.5 mg/kg of the selective 5-HT2CR antagonist, SB242084 (S0.5), mice exhibited significantly more HTRs than vehicle-treated mice. B) Though the effect was small, lorcaserin dose-dependently increased HTRs elicited by the psychedelic 5-HT2 agonist, DOI. Note that co-treatment with SB242084 and lorcaserin (S0.5/L3, S1/L3) caused much fewer HTRs than DOI (V/D1) or DOI plus lorcaserin (L1/D1, L3/D1, L5.6/D1). C) Lorcaserin (3 mg/kg) caused hypolocomotion, an effect reversed by co-treatment with SB242084 (S0.5/L3, S1/L3). D) When co-administered with DOI, lorcaserin dose-dependently decreased locomotor activity.
