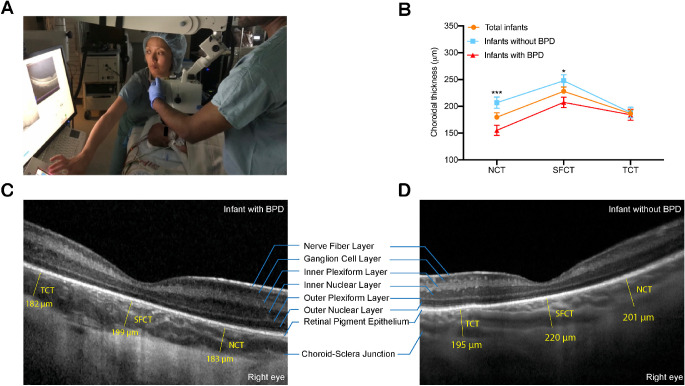
Figure 1.
(A) OCT imaging was performed in supine pediatric patients during examination under anesthesia using the Heidelberg Spectralis Flex Module. (B) Mean choroidal thickness at the nasal (NCT), subfoveal (SFCT), and temporal (TCT) locations by BPD status. Infants with BPD had thinner SFCT and NCT when compared with infants without BPD (*P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001, respectively). (C, D) Representative foveal B-scans of infants with and without BPD.