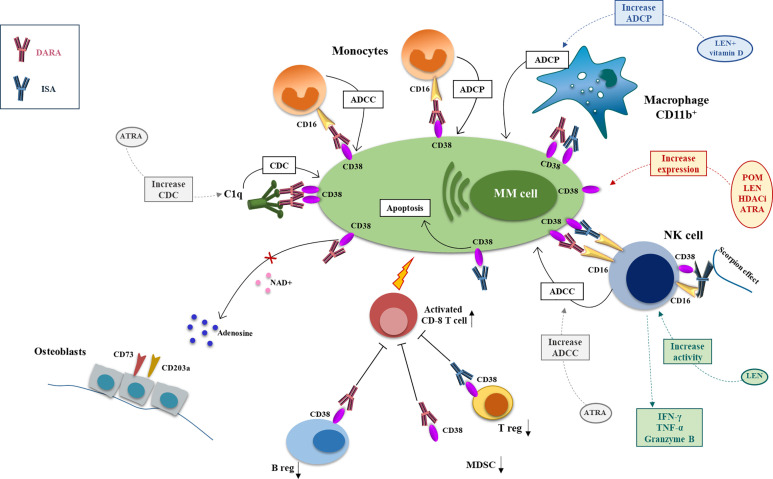
Figure 1.
Mechanism of action and major drug combination of anti-CD38 mAbs, daratutmumab, and isatuximab. The anti-CD38 mAbs exert their antimyeloma activity through different mechanisms of actions that can be potentiate by different anti-MM drugs. CDC is activated by engagement of the C1q by DARA and initiates the classical complement cascade and the recognition of MM cells by phagocytic cells and the production of the anaphylatoxins. This mechanism can be increased by ATRA. ADCC involves NK cell and monocytes that through CD16 recognize the anti-CD38 mAbs on MM cell surface and activate the cytotoxic process. ISA can activate directly the NK cells through the scorpion effect. NK cell activity can be boosted by ATRA and LEN. ADCP is carried by CD16+ monocytes and CD11b+ macrophage; LEN+ vitamin D can enhance anti-CD38 mAbs-mediated macrophages phagocytic activity. ISA can also have a direct anti-MM effect inducing MM cell apoptosis. DARA has also an immunomodulatory function downregulating the immunosuppressor ADO, diminishing Breg and MDSCs and activating CD8+ T cells. ISA exerts its immunomodulating potential downregulating Treg (DARA, daratumumab; ISA, isatuximab; CDC, complement depend cytotoxicity; ADCC, antibody depend cytotoxicity; ADCP, antibody depend phagocytosis; ATRA, all-trans retinoic acid; LEN, lenalidomide).