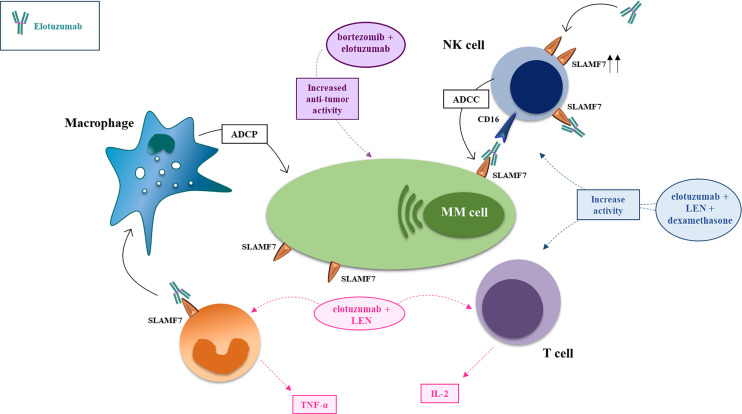
Figure 2.
Mechanism of action and major drug combination of the anti-SLAMF7 mAb elotuzumab. The anti-SLAMF7 mAb elotuzumab exerts anti-MM effects via several indirect mechanisms: (i) promoting macrophage-mediated antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP) engaging co-stimulatory signaling to enhance ADCP in macrophages expressing both SLAMF7 and EAT-2; (ii) facilitating NK cell-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) of myeloma cells through Fc-dependent interactions with CD16 (FcγRIIIA); (iii) enhancing co-stimulatory signaling in NK cells, thereby potentiating natural cytotoxicity of myeloma cells, via simultaneous engagement of ITAM-linked activating receptors on NK cells (e.g. NKp46 or CD16) with ligands on myeloma cells; (iv) tagging myeloma cells for cell recognition; (v) elimination of immunosuppressive CD8+CD28−CD57+ Tregs which overexpress SLAMF7. In combination with proteasome inhibitors (e.g. bortezomib, carfilzomib) or immunomodulators (e.g. lenalidomide, pomalidomide), elotuzumab enhances anti-tumor effects via activation of T-cells and NK-cells.