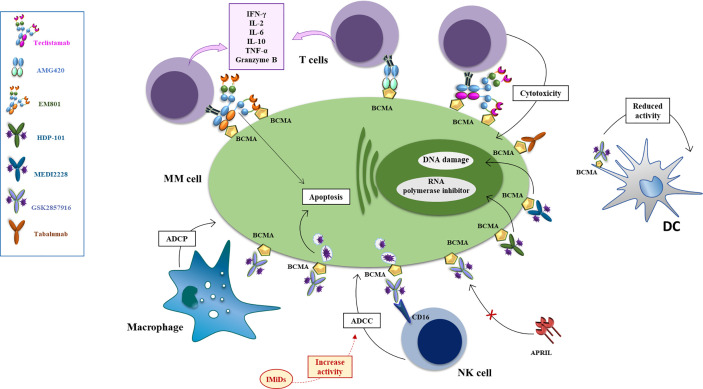
Figure 3.
Mechanisms of action of anti-BCMA mAb, antibody drug conjugates and bispecific antibodies. The antibody drug conjugate Belantamab mafodotin exerts anti-MM effect via several mechanisms: i. inducing ADCP via binding of the defucosylated Fc fragment of macrophages the arrest of MM cells in G2/M phase resulting in apoptosis; ii. inducing a powerful ADCC via binding of the defucosylated Fc fragment of NK and PBMC cells (an effect enhanced by combination with lenalidomide) iii. competing with BAFF and APRIL, reducing their signal of activation of NFkB in MM cells (an effect enhanced by combination with bortezomib) iv. reducing activity of BCMA+dendritic plasmacytoid cells which support proliferation and drug resistance of MM cells. Upon binding with MM cells via BCMA, MEDI2228 releases pyrrolobenzodiazepine to promote DNA damage and cell death, while HDP-101 releases the RNA polymerase inhibitor amanitin, to reduce transcription and protein synthesis, resulting in apoptosis of both rapidly dividing and resting cells. AMG 224 is an antihuman BCMA IgG1 antibody conjugated with mertansine, to inhibit the assembly of microtubules with consequent cell death. Tabalumab (LY 2127399) is an-anti BAFF human naked monoclonal antibody that neutralizes the membrane-bound and soluble forms of this factor, reducing their signal of activation of NFkB in MM cells. Bispecific monoclonal antibodies can simultaneously bind to two different types of antigen to engage effector cells against neoplastic cells. EM-801 and AMG-420 are two examples of BCMA/CD3 bispecific T-cell engager. Teclistamab is a BCMA/CD3 DuoBody.