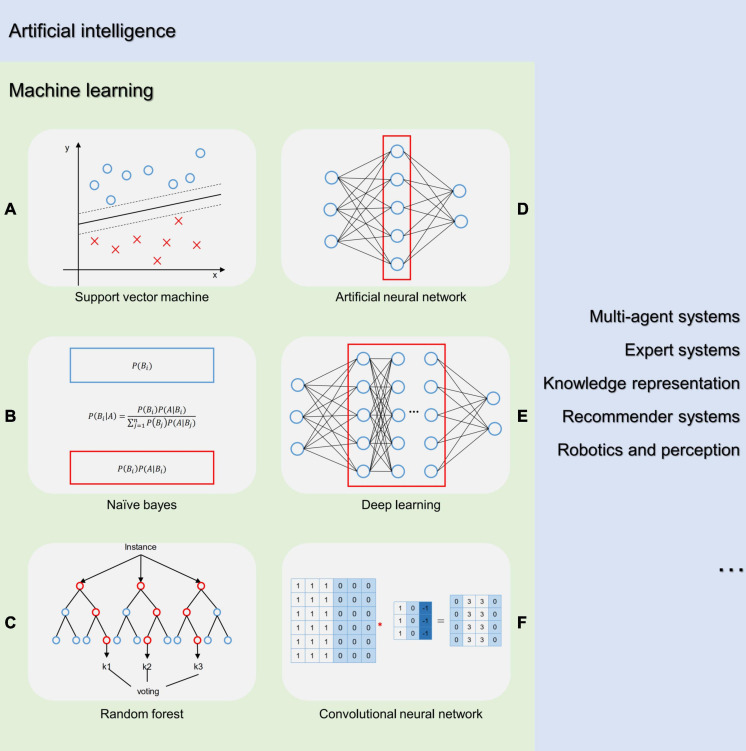
FIGURE 2.
Artificial intelligence terminology. AI is a general term concerning the computer science that enables the machine applying the human intelligence such as “learning” and “problem-solving” to perform the practical task. ML, multi-agent systems, expert systems, knowledge representation, recommender systems, robotics, and perception are the subset of AI. ML is a subset of AI, which automatically detects patterns in data to make predictions or decisions without explicitly being programmed. (A) Support vector machine (SVM) is a discriminative classifier that has an excellent performance in classification due to its strength of regularization and convex optimization. With the application of “kernel trick,” SVM can handle non-linear problems. (B) Naïve Bayes is a probabilistic ML algorithm based on the Bayes’ theorem and assumes the independence between features. (C) Random forest is an ensemble algorithm constructing numerous decision trees at training to increase the overall result by combining learning models. (D) Artificial neural network (ANN) is a regression and classification algorithm composed of artificial neurons applying simple classifiers to output decision signals based on the weighted sum of evidence. The basic structure was the combination of an input, hidden connection, and output layer. (E) Deep learning is a class of ANNs with several hidden layers which can learn complex hierarchical representations from the data for feature extraction and transformation, and for pattern analysis and classification. (F) Convolutional neural network (CNN) is a specific subset of ANNs that imitate the organization of the animal visual cortex for image processing tasks. The convolutional layer of CNN is the essential part.