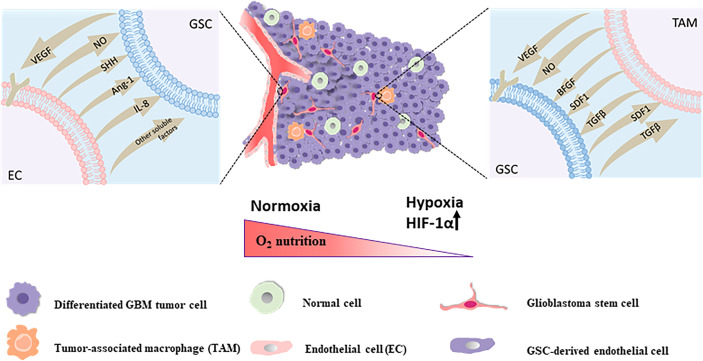
Figure 2.
The perivascular niche The self-renewal and maintenance of neighboring GSCs within the perivascular maintenance niche could been promoted via secretion of endothelial-derived diffusible signals including nitric oxide (NO), SHH, angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1), IL-8 and other soluble factors. GSCs are capable of stimulating the proliferation of endothelial cells and the sprouting of new vessels via secretion of VEGF and SDF-1 in the local tumor environment for sustainability and expansion of the vascular maintenance niche. The hypoxic niche With the constant invasion of GSCs, activation of hypoxia-related factors might take an active role in stemcell maintenance and one of the main factors is the hypoxia response Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1α (HIF-1α). The immune niche On the one hand, for TAMs, GSCs could chemo-attract and recruit TAMs to the tumor site, prompt the growth of macrophages and induce the polarization of TAMs into the immunosuppressive M2 phenotype through secreting chemokines and growth factors like VEGF, transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), SDF1 and soluble colony-stimulating factor 1 (sCSF-1). On the other hand, the accumulation of these pro-tumorigenic TAMs in tumor could secrete cytokines and signaling molecules such as basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), TGFβ, SDF1, VEGF, and nitric oxide (NO), contributing to tumor progression and GSCs maintenance in turn.