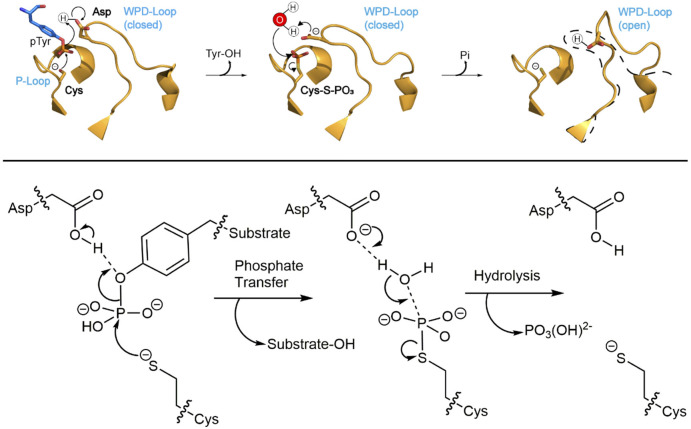
Figure 1.
Mechanism of the PTP-catalyzed reaction, showing the mobile WPD-loop, the phosphate-binding P-loop, as well as the substrate, nucleophilic water molecule, and key catalytic side chains. Motion of the protein loop bearing the conserved general acid (i.e., the side chains of residues D356 in YopH and D181 in PTP1B) brings it into position to function as a general acid in the first step, where it protonates the leaving group during formation of a phosphocysteine intermediate. In the second step, the carboxylate form activates a nucleophilic water molecule.