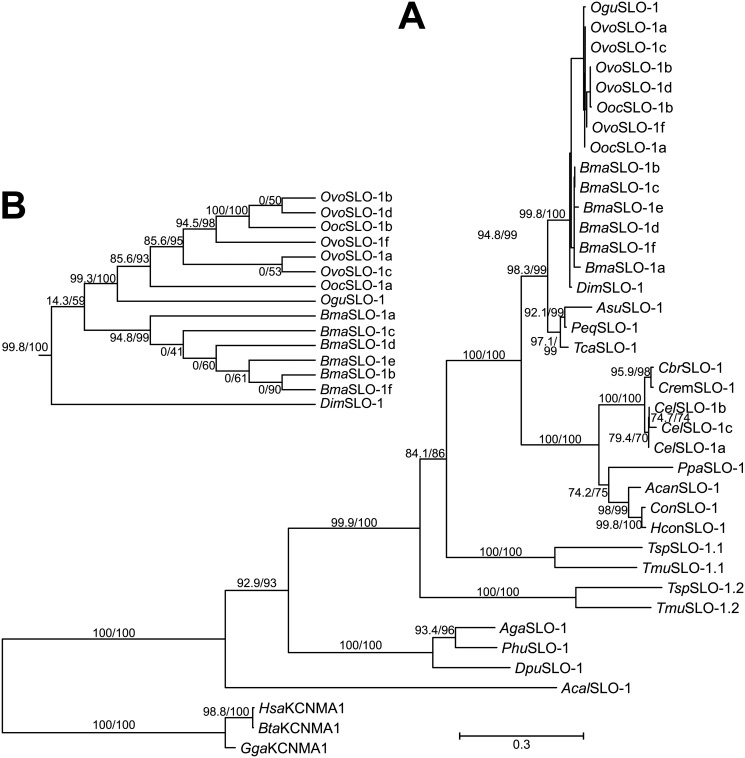
Fig 5. Phylogenetic analysis of nematode SLO-1 channels.
(A) Maximum likelihood phylogram calculated from full-length Slo-1 proteins. Slo-1 sequences from the nematode species Cel, Cbr, Cre, Pca, Hco, Con, Acan, Ovo, Ooc, Ogu, Bma, Dim, Tca, Peq, Asu, Tmu, and Tsu were aligned with orthologs from Dme, Aga, Phu, Dpu, Acal, Gal, Bta, and Hsa, representing an outgroup, using MCoffee [69]. For Onchocerca spp. and Brugia malayi, all splice variants were included, but only the variants slo-1a-c for Caenorhabditis elegans. For all other species, only a single splice variant was used per gene. Accession numbers are available in S1 Table. ModelFinder [70] was applied to identify the optimal amino acid substitution model. The VT+G4 amino acid substitution model was used with a Γ shape alpha set to 0.4242 and the 4 substitution relative rate categories (with equal frequencies) of 0.0203, 0.1996, 0.7562, and 3.0239. Maximum likelihood trees were calculated with IQ-TREE [71] using 2,000 iterations of the Shimodaira–Hasegawa modification of the approximate likelihood ratio test (before the slash) and 2,000 ultrafast bootstrapping replicates (behind the slash). The scale bar represents 0.3 substitutions per site. (B) Enlarged cladogram showing the relationship of filarial SLO-1 proteins. For clarity, node support values for this part of the tree are only indicated in B. Acal, Aplysia californica; Acan, Ancylostoma caninum; Aga, Anopheles gambiae; Asu, Ascaris suum; Bma, Brugia malayi; Bta, Bos taurus; Cbr, Caenorhabditis briggsae; Cel, Caenorhabditis elegans; Con, Cooperia oncophora; Cre, Caenorhabditis remanei; Dim, Dirofilaria immitis; Dme, Drosophila melanogaster; Dpu, Daphnia pulex; Gal, Gallus gallus; Hco, Haemonchus contortus; Hsa, Homo sapiens; Ogu, Onchocerca gutturosa; Ooc, Onchocerca ochengi; Ovo, Onchocerca volvulus; Pca, Pristionchus pacificus; Peq, Parascaris equorum; Phu, Pediculus humanus humanis; SLO-1, slowpoke big K+ conductance channel; Tca, Toxocara canis; Tmu, Trichuris muris; Tsu, Trichuris suis.