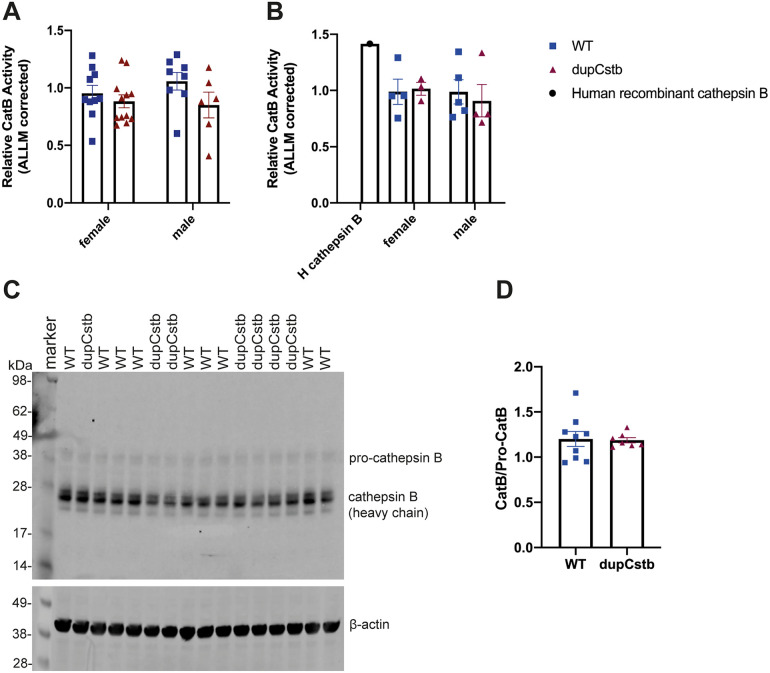
Fig 4. Activity of cathepsin B in cortical lysates of 3- and 6- month-old mice.
Total cortical proteins were used to determine enzyme activity, as the gain in fluorescence during the linear portion of the reaction curve relative to the wildtype mean. (A) Cortical relative cathepsin B activity at 3-months of age, graphed as group means ± SEM (n = 18 per genotype; (22 females and 14 males in total), revealed no statistically significant effects of dupCstb or sex (univariate ANOVA). (B) Cortical relative cathepsin B activity at 6-months of age, graphed as group means ± SEM, (dupCstb n = 7, wildtype n = 9; 7 females and 9 males in total), revealed no statistically significant effects of dupCstb or sex (univariate ANOVA). Recombinant human cathepsin B (R&D Systems, Cat. No. 953-CY-010) was used as a positive control. (C) Representative western blot probed with an anti-cathepsin B antibody that recognises pro-cathepsin B and cathepsin B heavy chain and an anti-β-actin antibody. (D) Protein band densities of pro-cathepsin B and cathepsin B heavy chain were quantified using ImageJ, normalised to β-actin, and are shown as cathepsin B/pro-cathepsin B ratio in the dupCstb group relative to the ratio in wildtype, graphed as group mean ± SEM (dupCstb n = 7, wildtype n = 9; 7 females and 9 males in total).