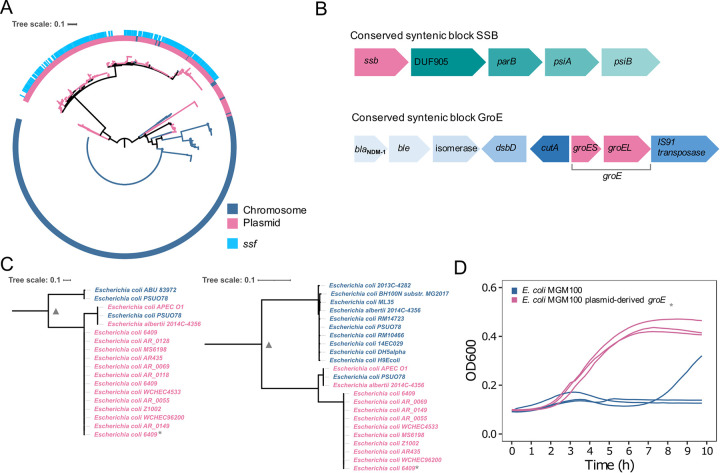
Fig 2. Phylogeny of plasmid-encoded essential genes in Escherichia.
A, Phylogeny of the single-stranded DNA-binding protein Ssb. Ssb homologs encoded on plasmid are shown in pink and encoded on chromosome are shown in blue. The plasmid ssb gene termed ssf is most abundant across the plasmid Ssb homologs. B, The conserved neighborhood (conserved syntenic block, CSB) of ssb and the chaperone groE encoded on plasmids (S3 and S4 Tables). C, Phylogeny of the chaperonin GroES (left) and GroEL (right). The triangle symbol marks the branch split that was constrained in the test for an alternative tree topology. D, Growth measurements of E. coli MGM100 and MGM100 carrying the plasmid-derived GroE (marked by *). The exceptional growth behavior observed in one E. coli MGM100 replicate should be considered an outlier since we found no evidence for other explanations to that result.