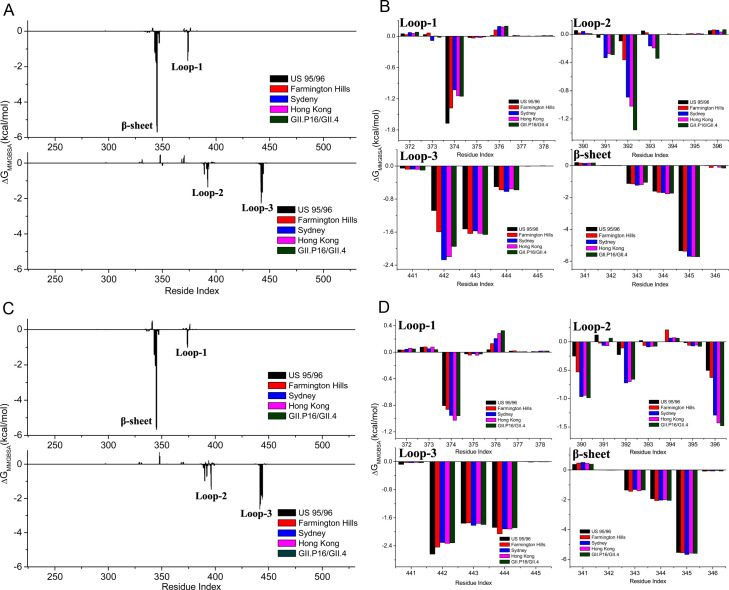
Fig 5. The per-residue energy decomposition analysis results.
(A) The per-residue contribution to the binding of type A HBGA for the various GII.4 strains. The upper and lower sub-figures correspond to the two dimeric P domains. (B) The type A HBGA binding free energy contributed by the residues in the binding pocket including loop-1 (residues 372–378), loop-2 (residues 390–396), loop-3 (residues 441–445) and an β-sheet (residues 341–346). (C) The per-residue contribution to the binding of type Ley HBGA for the various GII.4 strains. The upper and lower sub-figures correspond to the two dimeric P domains. (D) The type Ley HBGA binding free energy contributed by the residues in the binding pocket, i.e. loop-1 (residues 372–378), loop-2 (residues 390–396), loop-3 (residues 441–445) and an β-sheet (residues 341–346).