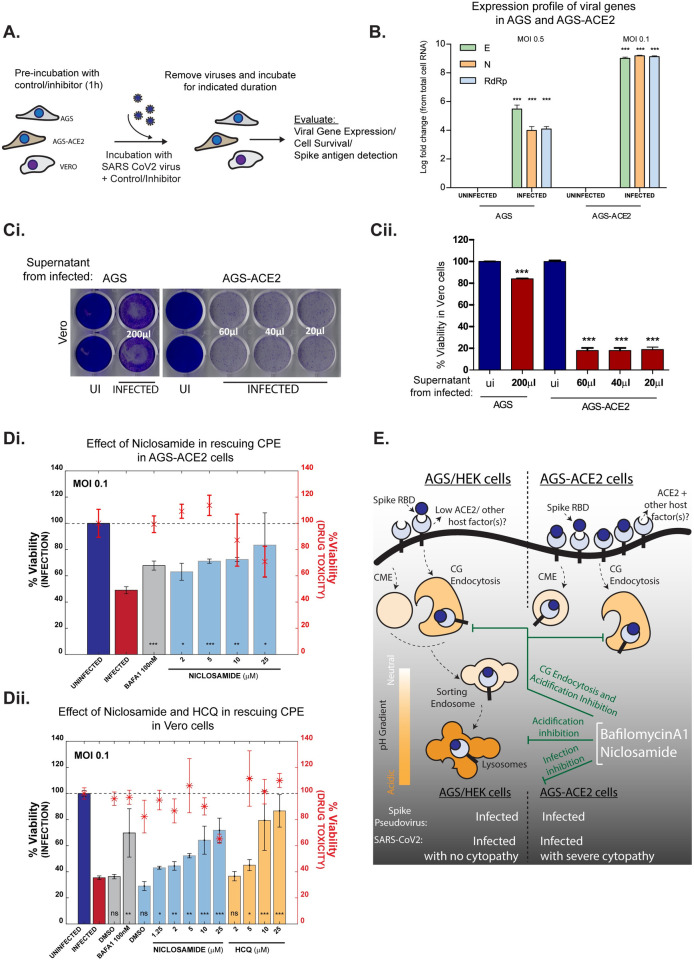
Fig 8. Validating the effect of endosomal acidification inhibitors on infection with SARS-CoV-2 virus.
A: Schematic of viral infection assays in three cell types: AGS, AGS-ACE2 and Vero. Cells were pre-treated with vehicle controls or inhibitors for 1 hour and then presented with viruses at specified MOI for indicated duration. Viruses were then removed, and cells were further incubated in presence or absence of inhibitors. Infection efficiency was estimated using viral gene expression, cell viability or immunostaining for Spike antigen. B: Viral gene expression from cell lysates of infected AGS and AGS-ACE2 cells depicted as log fold change with respect to uninfected controls. Expression is normalized to 18s rRNA levels. Cells were infected with viruses at MOI 0.5 for AGS and MOI 0.1 for AGS-ACE2 for 30 minutes, washed and further incubated for 18 hours. Number of repeats = 3 for all conditions. C: Evaluating infectability of supernatants from infected AGS and AGS-ACE2. AGS and AGS-ACE2 were initially infected with viruses at MOI 0.5 and MOI 0.1 respectively for 8 hours, viruses were then removed, and cells were further incubated for 24 hours. Indicated volumes of culture supernatants were used for infecting Vero cells for a total of 96 hours (for supernatant from AGS) and 72 hours (for supernatant from AGS-ACE2). Following this, Vero cells were stained with crystal violet to assess cell viability post infection. Image of the stained plate is shown in (i) and quantification in (ii). Number of repeats = 2 (AGS/Vero) and 3 (AGS-ACE2 /Vero) for both uninfected and infected conditions. D: Assessing effect of endosomal acidification inhibitors on viral infection. AGS-ACE2 (i) and Vero cells (ii) were pre-treated with control or inhibitors for 1 hour followed by presentation of viruses at MOI 0.1 for 30 minutes (AGS-ACE2) or 8 hours (Vero) in the presence or absence of inhibitors. Viruses were removed and cells further incubated for 16 hours (AGS-ACE2) or 48 hours (Vero) and cell viability assessed by ATP quantification assay. Number of repeats = 3 for each condition. Bars represent mean +/- SD of % viability upon infection. Asterix with error bars in red represents the mean +/- SD of % viability indicating drug toxicity in the absence of viruses. E: In cells expressing low endogenous ACE2, Spike RBD endocytosis is aided by ACE2/other host cell factors via the CLIC/GEEC pathway. Overexpression of ACE2 results in trafficking of RBD through both CG and CME pathways. Acidification inhibitors BafA1 and FDA approved drug Niclosamide, neutralize the pH of endosomes as well as block entry via the CG pathway. Infection assays using both Spike pseudovirus and infectious SARS-CoV-2 virus confirm that BafA1 and Niclosamide prevent viral infection.