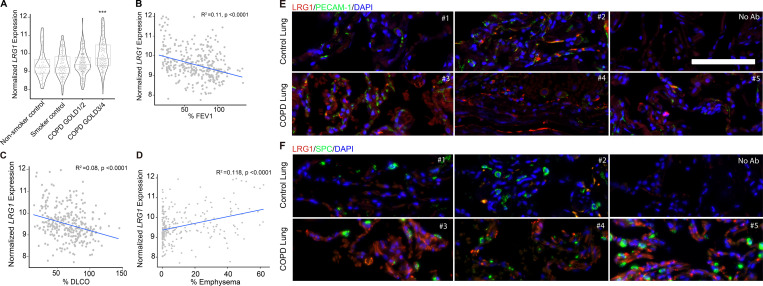
Figure 6.
LRG1 levels are up-regulated in human COPD tissue and directly correlate with severity of disease and lung function decline. (A) In silico analysis from LGRC of expression of LRG1 mRNA in nonsmoker control, smoker control, COPD GOLD1/2, and COPD GOLD3/4 lungs. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Generalized linear model Wald statistics were used to assess significance of coefficients in relevant models (***, P < 0.001). (B–D) Correlation between the expression of LRG1 and DLCO, FEV1, and severity of emphysema observed on chest computed tomography. Generalized linear model Wald statistics were used to assess the significance of coefficients in relevant models. (E and F) Representative immunofluorescent staining images of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human COPD lung tissue obtained from LTRC (as described in Materials and methods). Individual control and COPD patient samples were stained for total levels of LRG1 (red), PECAM-1 (top panel, green), DAPI (blue), and SPC (bottom panel, green). Scale bar, 100 µm.