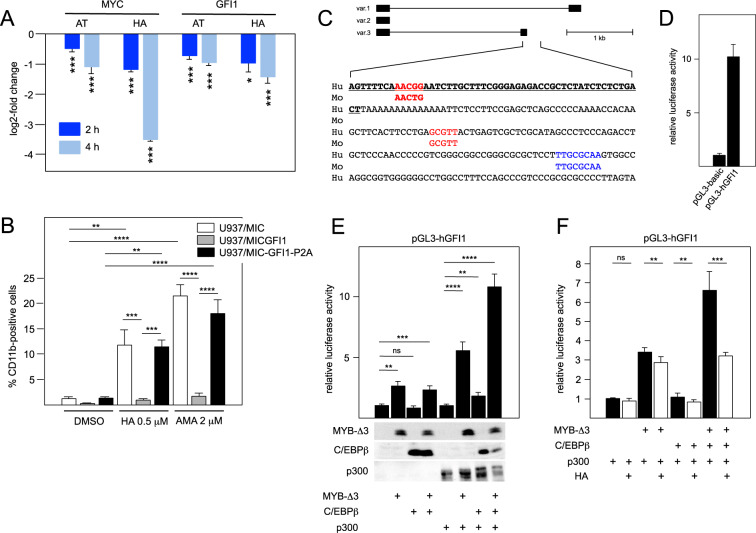
Fig. 6. C/EBPβ-inhibitory STLs induce CD11b and CD14 expression in U937 cells by down-regulating GFI1 expression.
A Decreased MYC and GFI1 expression in U937 cells after treatment for 2 and 4 h with AT (1 μM) or HA (0.5 μM). Statistical significance (*p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, Student’s t test). B U937 cells expressing ectopic wild-type GFI1 (U937/MIC-GFI1), an inactive mutant of GFI1 (U937/MIC-GFI1-P2A) or no GFI1(U937/MIC) were analyzed by flow cytometry for CD11b expression. The bars indicate the percentage of CD11b positive cells after treatment for 4 days with DMSO, 0.5 μM HA or 2 μM AMA. Statistical significance was determined with one-way ANOVA with Tukey correction (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001). C Schematic illustration of GFI1 transcript variants and nucleotide sequence of the GFI1 variant 3 promoter region. Bold underlined letters correspond to the 5’ end of human GFI1 variant 3 mRNA. Sequences in red and blue mark MYB and C/EBPβ binding sites, respectively. Conservation of these sequences in the mouse genome is indicated below. D Comparison of the luciferase activity of the cloned GFI promoter and the promoter-less luciferase vector. E, F Reporter assays of the human GFI1 promoter in the presence of the indicated combinations of expression vectors for MYB-Δ3, C/EBPβ, and p300. In panel E, Western blotting (bottom) confirms the expression of the indicated proteins. Reporter assays in panel (F) were performed without or with 1 μM HA. Asterisks in panels (E) and (F) indicate statistical significance (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, Student’s t test; NS, non-specific).